A Crypto coin, although introduced with many advantages, cannot avoid shortcomings which become apparent during user interaction. Even major cryptocurrencies like Ethereum are not exempt. Therefore, to address these issues, Ethereum has undergone multiple Hard Forks, each bringing it closer to its goals. Let’s explore what Ethereum Hard Fork is, the history of its upgrades, and the necessity of Hard Forks in the article below.
What is Ethereum Hard Fork?
Ethereum Hard Fork refers to a change in the rules currently applied to the Ethereum blockchain to set new standards. This change causes the Blockchain platform to no longer operate under previous regulations, meaning some transactions and data types are not accepted on the chain. Unlike other Blockchains, Ethereum’s Hard Forks are planned in advance, with the new Blockchain following the chain after the fork.
The diagram below illustrates this more visually and clearly:
History of Ethereum Hard Forks
Homestead
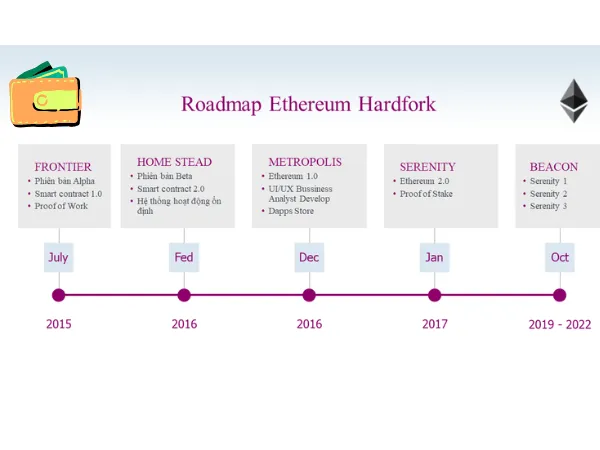
The first Hard Fork of Ethereum occurred on 14/05/2016, at Block 1,150,000. This fork changed Ethereum from Frontier to Homestead with key updates:
- Elimination of Canary Contract feature
- Launch of new code in Solidity programming language
- Launch of Mist wallet, supporting users to store and transfer ETH, and create and execute Smart Contracts
DAO Hard Fork
Unlike the first, the second Hard Fork of Ethereum was after an unintended incident known as The DAO Hack.
To recover the stolen funds, the Ethereum developers decided to perform a Hard Fork. As a result, Ethereum’s blockchain was split into two different chains: Ethereum (the original chain) and Ethereum Classic (the new chain).
Tangerine Whistle
The third Hard Fork of Ethereum is called EIP-150 Hard Fork or Tangerine Whistle.
This took place at block 2,463,000 on 18/10/2016. Its main focus was on updating gas fees across the network to solve the DoS attack issue.
Spurious Dragon
The next Hard Fork, named Spurious Dragon, happened at block 2,675,000. This included the official implementation of new EIPs on Ethereum’s Blockchain.
The new EIPs include:
- EIP-155: Ensures transactions on Ethereum are not replayed on alternative chains.
- EIP-160: Calculates EXP fee based on computational complexity, with higher complexity attracting higher fees.
- EIP-161: Supports cleaning up large amounts of empty accounts from DoS attacks.
- EIP-170: Changes (either diminishes or enlarges) the maximum code size allowed for contracts on the Ethereum blockchain.
Byzantium
The fifth Hard Fork took place at block 4,370,000, introducing 9 notable EIPs aimed at enhancing security and scalability.
Constantinople
The sixth and significant Hard Fork aimed to transition Ethereum’s consensus mechanism from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake. It was executed after multiple delays on 16/01/2019 at block 7,080,000, with updates involving 4 EIPs:
- EIP-145 and EIP-1052: Optimize gas usage and address DoS attack issues
- EIP-1014: Support activation of layer2 solutions
- EIP-1234: Reduce mining difficulty and block rewards from 3 ETH to 2 ETH
Istanbul
The latest Hard Fork of Ethereum was at block 9,069,000, introducing updates via 6 EIPs:
- EIP-152: Enable Ethereum compatibility with ZCash and other Equihash chains
- EIP-1108: Support gas fees for STARKs and SNARKs, reducing costs
- EIP-1344: Enhance security with blockchain identity to prevent cross-chain attacks
- EIP-1844: Regulate gas fees for certain EVM operations to prevent attacks and balance network resources
- EIP-2028: Reduce costs for deploying zk-SNARK and zk-STARK contracts
- EIP-2200: Modify the method for computing storage fees in EVM
What are the effects of Hard Forks?
Ethereum faces stiff competition from EOS, Zilliqa, Cardano etc.
In reality, the forks risk diluting the overarching network that the main Blockchain provides, especially as most Cryptos have plummeted in value up to 90%. Currently, developers are working on creating new chains.

The situation could turn disadvantageous for Ethereum if competitors continue to expand aggressively and dominate the market, leading to the community being split and lacking cohesion, unlike platforms like EOShay and Cardano.
Regarding Ethereum’s price, predictions about its long-term future post-Hard Fork are largely uncertain, as the price varies without clear basis. However, short-term analysis shows some noticeable changes, as the user community tends to focus more on coins that have recently undergone upgrades.

This could be good news for new cryptocurrencies launched after Ethereum’s successful Hard Fork. Additionally, the Hard Fork facilitates Ethereum’s transition from PoS to PoW, which could be a key driver for short-term price increases.
It’s difficult to exactly predict which Ethereum chain will impact the network or prices in the short or long term. However, it is crucial to monitor whether Ethereum will continue to dominate Dapp development in the near future.
Why is Ethereum Hard Fork necessary?
As mentioned, Hard Fork is an upgrade process for Ethereum intended to improve features and fix existing issues, adapting to market demands and enhancing Ethereum’s capabilities.
The Hard Fork of Ethereum is well-planned, so usually, unexpected issues are minimal during this process.
Though there have been cases of unexpected Hard Forks, as with the second, these still occur successfully, and Ethereum is progressively achieving its goal of shifting to PoS, expected to be accomplished after just two more Hard Forks.
Post-Hard Fork Changes in Ethereum
ETH Price
Generally, Ethereum’s price remains relatively stable, experiencing slight decreases or occasional minor increases after each Hard Fork.
Dapps
After each upgrade, all Dapps need to update to utilize new features and comply with new regulations on the Ethereum Blockchain. For example, failure to update could mean that Smart Contracts within Dapps are no longer executable.
Miners
A Hard Fork brings Ethereum closer to its goal of PoS, representing a step back for miners currently active on Ethereum.
Conclusion
This article has covered key issues regarding Ethereum Hard Fork, including its definition, upgrade history, necessity, and the benefits it brings. Hopefully, it provides new insights and answers your questions.
See more: Hard Fork




