If you’re new to cryptocurrency, one of the first questions you might ask is, what is a bitcoin wallet? Simply put, a bitcoin wallet is a digital tool that allows you to store, send, and receive bitcoin securely. Unlike a physical wallet that holds cash, a bitcoin wallet doesn’t actually store the bitcoins themselves. Instead, it safely manages the private keys that grant you access to your cryptocurrency on the blockchain.
Understanding what a bitcoin wallet is and how it works is essential for anyone who wants to start using bitcoin, whether for investment or everyday transactions. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about bitcoin wallets in 2025, from types of wallets to how to keep your crypto safe.
1. What is a bitcoin wallet? Why do bitcoin wallets matter?
If you’re new to the world of cryptocurrency, you might be wondering: what is a bitcoin wallet? Is it like the wallet in your pocket? The answer is yes and no. A bitcoin wallet doesn’t store physical bitcoins (as they don’t exist in physical form) but instead holds the keys that let you access and control your bitcoins on the blockchain. Without a bitcoin wallet, you simply can’t own, send, or receive bitcoin.
Think of a bitcoin wallet as your personal gateway to the decentralized world of cryptocurrencies. Just like your debit card connects you to your bank account, a bitcoin wallet connects you to your digital assets. However, there’s a crucial difference: banks control debit cards, but you alone control your bitcoin wallet as long as you hold the private keys.

This concept of ownership is what makes bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies revolutionary. It removes the need for intermediaries like banks or brokers, giving you full control over your money. But with that power comes responsibility understanding how wallets work is essential for protecting your crypto from theft, loss, or mistakes.
In the next section, we’ll break down exactly how bitcoin wallets function under the hood, from wallet addresses to private keys.
2. Bitcoin wallets explained: How they really work
To understand what a bitcoin wallet truly is, let’s go beyond the basic definition. A bitcoin wallet doesn’t store actual coins like a leather wallet stores cash. Instead, it stores a pair of cryptographic keys: one public and one private. These keys are what allow you to interact with the Bitcoin blockchain.
Every bitcoin wallet is made up of:
- A public bitcoin address: This is like your bank account number. You can share it with others so they can send you bitcoin. It typically looks like a long string of letters and numbers (e.g., 1A1zP1eP5QGefi2DMPTfTL5SLmv7DivfNa).
- A private key: This is the secret password that proves you own the funds linked to your public address. If someone gains access to this, they can steal your bitcoin. Private keys are often expressed as a 256-bit number or transformed into a recovery phrase (typically 12–24 words).

Your private key or recovery phrase = your funds. Never share it. Never lose it.
Bitcoin wallets manage these keys on your behalf. Modern wallets typically hide the technical complexity and allow users to interact through a simple interface like copying a wallet address or scanning a QR code.
What is a bitcoin wallet address?
A bitcoin wallet address is the public-facing identifier used to receive bitcoin. It’s derived from the public key and allows others to send BTC to your wallet. Although it might look random, it’s mathematically linked to your private key. You can think of it as your crypto “email address,” while the private key is your password.
There are several formats of bitcoin addresses:
| Address Format | Example Prefix | Description |
| Legacy | 1… | Older format, still in use |
| SegWit | 3… | More efficient, lower fees |
| Bech32 | bc1… | Latest format, best for fees and compatibility |
Pro tip: Always double-check the format your wallet or exchange supports before sending BTC.
Next, we’ll explore different types of bitcoin wallets, from apps to hardware devices and how to choose the right one for your needs.
3. Types of bitcoin wallets: Choosing what’s right for you
Not all bitcoin wallets are the same. The type of wallet you choose can significantly impact your security, convenience, and control over your funds. Each wallet type offers a different balance between accessibility and protection.
3.1. Software wallets
Software wallets are applications or programs installed on your device whether that’s a desktop, smartphone, or web browser. These are among the most popular choices for beginners due to their ease of use and free access.
There are three main types of software wallets:
- Desktop wallets: Installed on your PC or laptop, offering full control but vulnerable if your computer is hacked or infected with malware.
- Mobile wallets: Convenient for daily use, these wallets use your phone to send and receive BTC on the go. Most allow you to scan QR codes and enable biometric login.
- Web wallets: Accessed via a browser, these are easy to use but often considered the least secure, as they may store your keys on a remote server.
Always enable 2FA and use strong passwords when using software wallets.
Popular examples: Electrum, Exodus, Trust Wallet, and the Bitcoin.com Wallet app.

3.2. Hardware wallets
Hardware wallets are physical devices designed specifically to store your private keys offline. They offer the highest level of security by isolating your private keys from internet-connected devices.
When you want to make a transaction, you plug the wallet into your computer or connect via Bluetooth. It will sign the transaction without exposing your keys.
Advantages:
- Immune to most types of malware.
- Ideal for long-term storage or large amounts of bitcoin.
Disadvantages:
- Costs between $50 and $200.
- Not as convenient for everyday transactions.
Popular devices: Ledger Nano S/X, Trezor Model T.

3.3. Paper wallets (deprecated)
A paper wallet is a printed copy of your public and private keys. While this method was once popular, it’s now considered outdated and risky due to:
- Easy to lose, tear, or damage.
- Not suitable for frequent transactions.
- No password protection if someone finds it, your funds are gone.
Most experts do not recommend using paper wallets today.

3.4. Custodial vs non-custodial wallets
Another critical distinction is who controls your private keys:
| Type | Who holds the keys? | Pros | Cons |
| Custodial | A third party | Easy to recover access | Less control, higher risk of hacks |
| Non-custodial | You (the user) | Full control, no third-party risk | Requires more responsibility |

For true financial sovereignty, non-custodial wallets are ideal but only if you’re ready to take full responsibility for your keys.
4. How to create and set up a bitcoin wallet [step-by-step]
Setting up a bitcoin wallet doesn’t require any technical background. Whether you’re using a smartphone or computer, the process is fast, free, and beginner-friendly. Follow this simple guide to get started safely.
Step 1: Choose the right type of wallet
Before setting up, decide on the type of wallet that fits your needs:
- For everyday use: Mobile or desktop software wallet
- For long-term holding: Hardware wallet
- For convenience but less control: Custodial wallet
- For full control and privacy: Non-custodial wallet
Tip: Beginners often start with a trusted mobile wallet like the Bitcoin.com Wallet or Trust Wallet, then upgrade to a hardware wallet later.
Step 2: Download or buy your wallet
Depending on the wallet type:
- Software wallets: Visit the official website or app store. Always verify you’re downloading from the legitimate source.
- Hardware wallets: Purchase directly from the manufacturer (e.g., ledger.com, trezor.io) never buy secondhand.
Step 3: Create your wallet
Open the wallet app or plug in your device and follow the setup instructions. This typically involves:
- Creating a new wallet
- Setting a strong password or PIN
- Writing down your recovery phrase (12–24 secret words)
Never store your recovery phrase online or in plain text. Write it down and store it in a secure, offline location.
Step 4: Backup your wallet
Most wallets will prompt you to back up your wallet using the recovery phrase. This step is critical: if your device is lost, stolen, or broken, this is the only way to recover your bitcoins.
Some wallets, like the Bitcoin.com Wallet, offer cloud backup options encrypted with a password. Use this only if you trust the security of your cloud account and password manager.
Step 5: Receive your bitcoin wallet address
Once set up, your wallet will generate at least one bitcoin wallet address, a unique string of characters used to receive funds. It looks like this:
bc1qxyz… or 1A1zP1eP5QGefi2DMPTfTL5SLmv7DivfNa
This is your public wallet address you can safely share it with others when receiving BTC. It’s similar to a bank account number, but without a name attached.
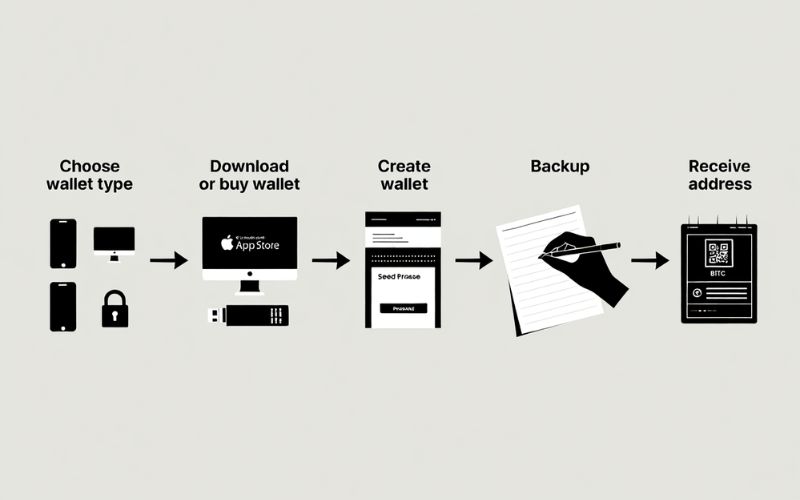
Now you’re ready to send, receive, and manage bitcoin securely.
5. How to use your bitcoin wallet safely
Using your Bitcoin wallet properly is essential to keep your funds secure and avoid common mistakes that new users make. Here’s a straightforward guide to help you handle your wallet safely.
5.1. Sending and receiving bitcoin
Bitcoin wallets allow you to send and receive bitcoins easily:
- To receive bitcoin:
Share your bitcoin wallet address (public address) with the sender. This address is a long string of letters and numbers unique to your wallet. Always double-check the address before sharing to avoid mistakes. - To send bitcoin:
Enter the recipient’s bitcoin address in your wallet app, specify the amount, and confirm the transaction. Most wallets show a transaction fee which goes to miners for processing your transfer on the blockchain.
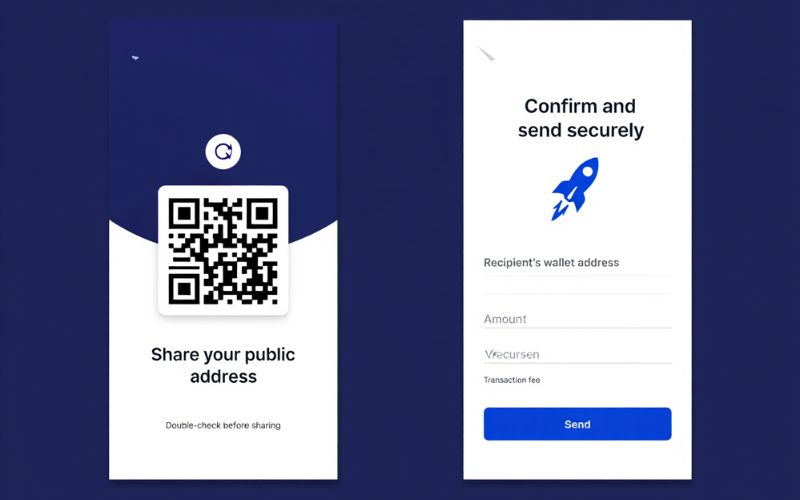
Tip: Always send a small test amount first if you’re sending to a new address, especially if the amount is significant.
5.2. Backup & security tips
Protecting your bitcoin wallet is vital:
- Keep your recovery phrase offline: Write it down on paper and store it in a safe place. Never share it or store it digitally without encryption.
- Use strong passwords and two-factor authentication (2FA): For software wallets or custodial accounts, enable 2FA wherever possible.
- Update your wallet software regularly: This ensures you have the latest security features and patches.
- Beware of phishing attacks: Always access your wallet app or website directly, not via suspicious links or emails.
- Consider hardware wallets for large holdings: Hardware wallets keep your private keys offline and away from hackers.
Following these steps helps you keep your bitcoins secure while enjoying the benefits of decentralized digital money.

6. Bitcoin wallet vs bitcoin exchange account: what’s the difference?
For beginners exploring Bitcoin, understanding the difference between a bitcoin wallet and a bitcoin exchange account is crucial. While both are used to manage your bitcoins, they serve different purposes and offer different levels of control and security.
As covered earlier, a bitcoin wallet is a tool that allows you to store your private keys, enabling you to send, receive, and control your bitcoins directly. You fully own the bitcoins associated with your wallet and are responsible for securing your private keys or recovery phrase.
A bitcoin exchange account is an account you create on a cryptocurrency exchange platform such as Coinbase, Binance, or Kraken. These platforms act as intermediaries:
- They hold your bitcoins on your behalf (custodial service).
- You can buy, sell, and trade bitcoins through the exchange interface.
- Your private keys are controlled by the exchange, not you.
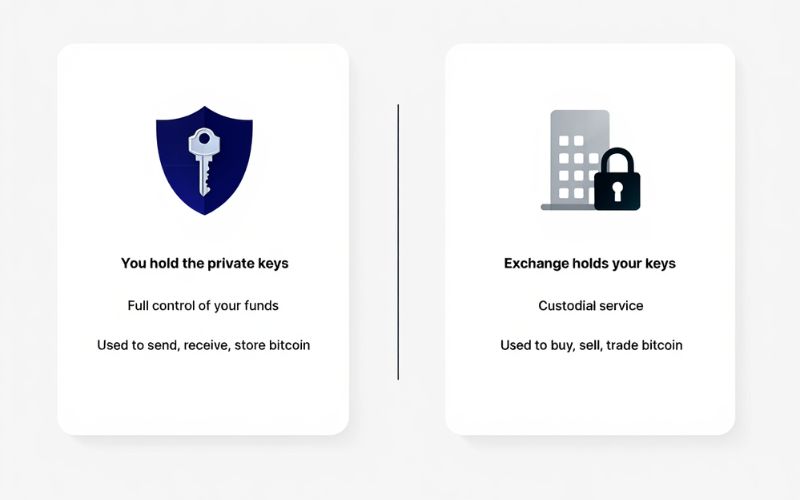
Key differences summarized:
| Aspect | Bitcoin Wallet | Bitcoin Exchange Account |
| Ownership | You control your private keys | Exchange controls private keys |
| Security responsibility | Fully your responsibility | Exchange responsible for wallet security |
| Control over funds | Full control | Limited control, subject to exchange rules |
| Usage | Sending/receiving, storing bitcoins | Buying, selling, trading cryptocurrencies |
| Risk | Risk if private keys lost or stolen | Risk if exchange is hacked or insolvent |
Which should you use?
- If you want full control over your bitcoins and prioritize security, a personal bitcoin wallet is best.
- If you want to trade frequently or buy/sell easily without managing private keys, an exchange account is more convenient.
Always remember, “Not your keys, not your coins” – meaning if you don’t control the private keys, you don’t fully control the bitcoins.
Read more:
- What do you do with Bitcoins? 6 profitable secrets you should know in 2025
- How to Buy Bitcoins in 2025 – Step by Step Guide for Beginners
- What is Bitcoins address? A beginner-friendly guide to crypto wallets
7. Common questions about bitcoin wallets (FAQs)
To help beginners better understand bitcoin wallets, here are answers to some of the most frequently asked questions.
7.1. What is a bitcoin wallet address?
A bitcoin wallet address is a unique string of letters and numbers that functions like an account number for your wallet. It’s used to receive bitcoins from others. You can share your wallet address publicly without risking your funds.
7.2. What is the difference between a bitcoin wallet and a bitcoin wallet address?
A bitcoin wallet is the tool or program that manages your bitcoins and private keys. The bitcoin wallet address is just the public identifier where others send bitcoins to you.
7.3. Can I have more than one bitcoin wallet address?
Yes. Most wallets generate multiple addresses for you to enhance privacy and security. You can use different addresses for different transactions.
7.4. Is a bitcoin wallet the same as a bank account?
Not exactly. Unlike a bank account, a bitcoin wallet does not store bitcoins but stores your private keys which allow you to access bitcoins on the blockchain. You have full control, but also full responsibility.
7.5. What happens if I lose my bitcoin wallet?
If you lose access to your wallet and don’t have a backup of your private key or recovery phrase, your bitcoins are lost permanently. This is why backing up your wallet safely is essential.
7.6. Are bitcoin wallets safe to use?
Bitcoin wallets can be very secure if you follow best practices like using hardware wallets for large amounts, never sharing your private keys or recovery phrase, and enabling extra security features.
8. Final thoughts: Do you really need a bitcoin wallet?
For anyone interested in owning, sending, or receiving bitcoin, understanding what is a bitcoin wallet is essential. A bitcoin wallet is your gateway to managing your cryptocurrency safely and independently. While exchanges provide convenient platforms to buy and sell bitcoin, having your own wallet gives you full control over your funds and greater security.
Choosing the right wallet type depends on your needs whether you prioritize ease of use or top-level security. Remember, the safety of your bitcoins depends largely on how well you manage your wallet’s private keys and recovery phrases.
In 2025 and beyond, as cryptocurrencies become more mainstream, a bitcoin wallet will remain a fundamental tool for anyone serious about participating in the crypto space. If you’re just starting, take your time to learn how wallets work and pick one that fits your comfort and security preferences.
For more beginner-friendly guides on bitcoin and crypto, explore our other articles on Vietnam U.S. Trade.






