What is the difference between symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption, and why does it matter in 2025? Symmetric encryption uses one shared key, while asymmetric encryption uses a key pair each suited for different digital security needs.
In today’s world of rising cyberattacks and data breaches, choosing the right encryption method can protect your personal data, business assets, and online identity. Understanding these two core encryption types will help you avoid vulnerabilities, save costs, and ensure trust in digital communication.
Let’s break down how they work, when to use each, and why this matters more than ever with practical guidance from the team at vietnam-ustrade.
1. What is symmetric encryption?
Let’s explore the basic concept, common algorithms, and real-world uses of symmetric encryption below.
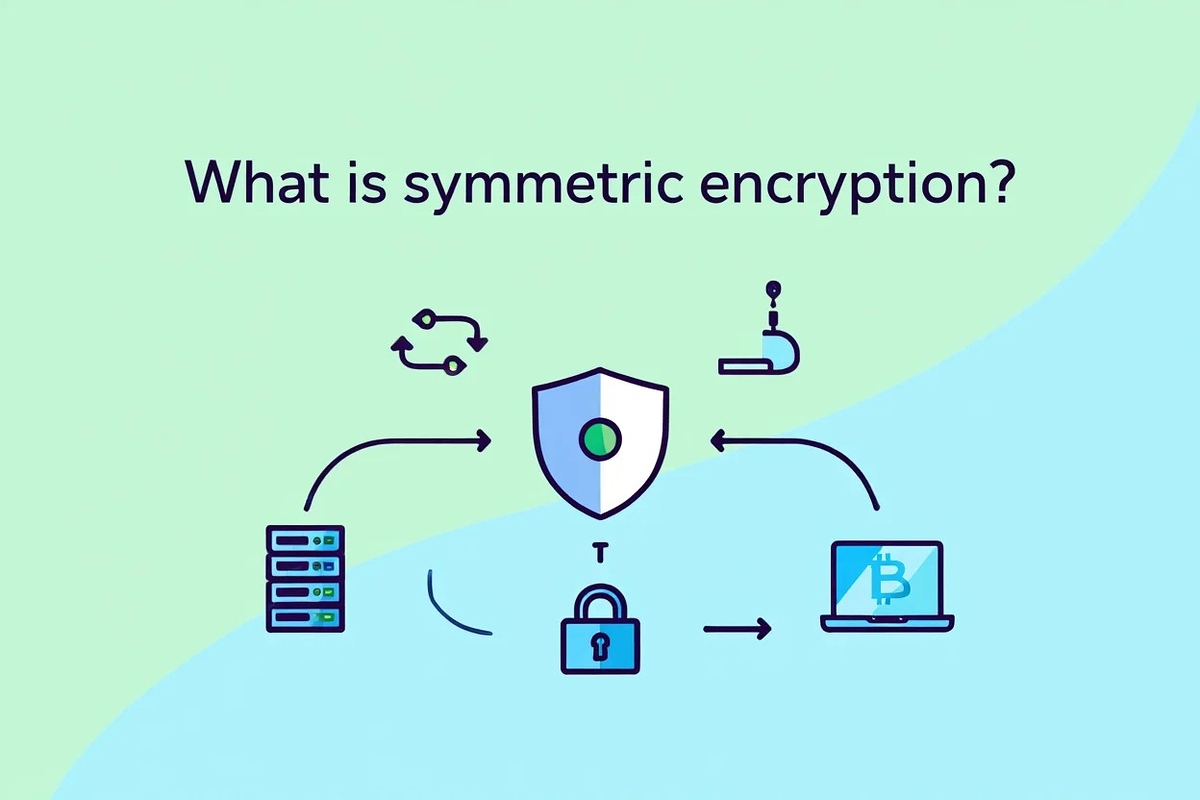
1.1 Definition and basic process
Symmetric encryption uses a single secret key for both locking (encrypting) and unlocking (decrypting) information. The process is straightforward: plain data (plaintext) is transformed into a coded form (ciphertext) using the key and then returned to its original form using the same key. This method is favored for its simplicity and ability to handle large amounts of data quickly.
1.2 Common symmetric encryption algorithms
Here are widely used symmetric encryption algorithms:
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) – Established as the global standard since 2001
DES (Data Encryption Standard) – Developed in the 1970s, now mostly outdated
3DES (Triple DES) – A more secure version of DES, still in limited use
RC4 – Previously popular streaming cipher, less secure today
1.3 Real-world use cases
Symmetric encryption is commonly used for:
• Encrypting files and entire disk drives for data protection
• Securing Virtual Private Network (VPN) connections
• Protecting sensitive database information
These real-world examples highlight the importance of knowing the difference between symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption when selecting the right solution.
2. What is asymmetric encryption?
Here’s a breakdown of how asymmetric encryption works, the algorithms it uses, and its real-world applications.
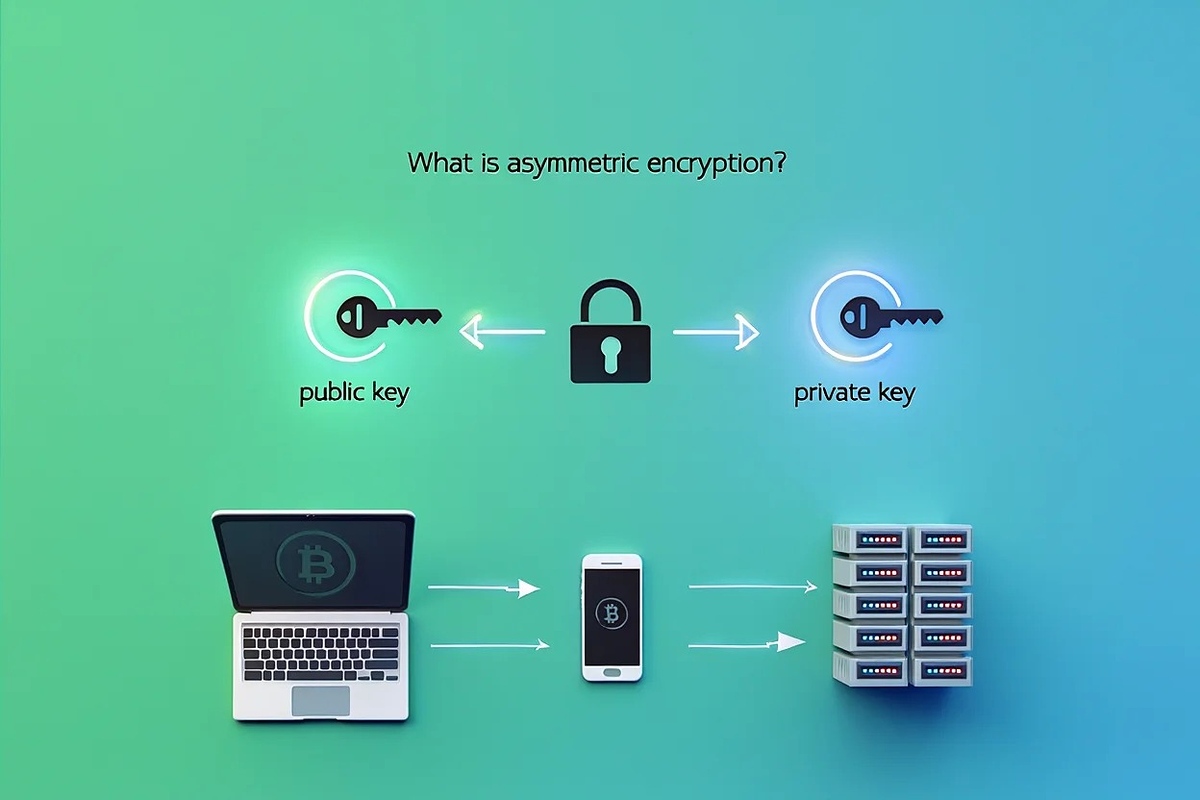
2.1 Definition and basic process
Asymmetric encryption uses two keys: a public key to lock (encrypt) data and a private key to unlock (decrypt) it. Anyone can use the public key to send a secure message, but only the private key owner can read it. The flow is: plaintext is encrypted with the public key, producing ciphertext, which only the private key can decrypt. This allows secure communication without sharing secret keys upfront.
2.2 Common asymmetric encryption algorithms
Popular asymmetric algorithms include:
RSA – Most widely known, often used for digital signatures and secure key exchanges (2048-bit keys typical)
ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) – Efficient with smaller keys, popular for mobile devices
Diffie-Hellman – Common for securely agreeing on shared secrets
ElGamal – Used in some encryption and digital signature applications
2.3 Real-world use cases
Examples where asymmetric encryption is essential:
• Securing websites through SSL/TLS protocols
• Encrypting email communications
• Verifying software authenticity with digital signatures
Choosing asymmetric encryption for these cases reinforces the difference between symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption in terms of security and key management.
3. Difference between symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption
The table below clearly outlines the difference between symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption based on key features, speed, and use cases. Here’s a clear comparison between the two main encryption types:
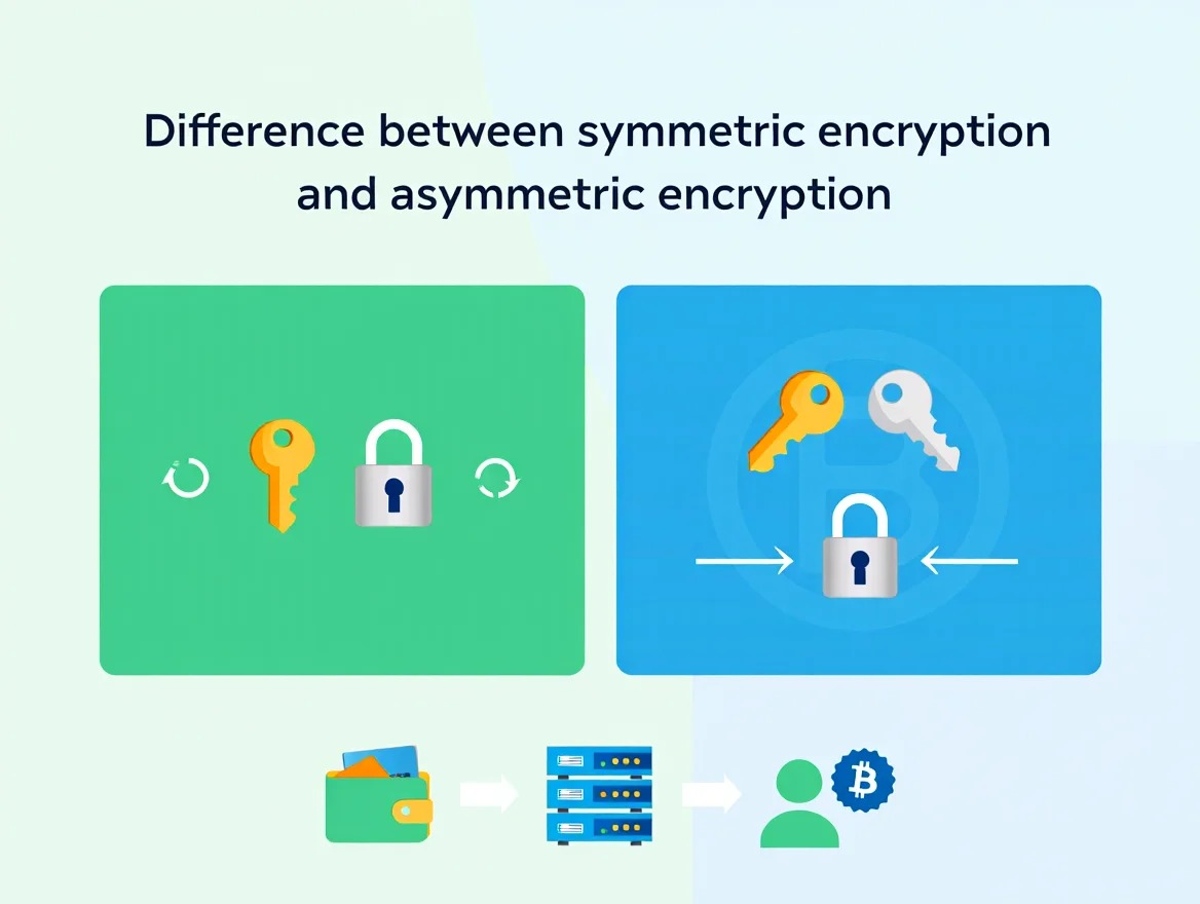
| Feature | Symmetric Encryption | Asymmetric Encryption |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Keys | 1 (shared secret key) | 2 (public and private key pair) |
| Speed | Fast and efficient | Slower due to complex math |
| Security Risk | Key must be securely shared | Safer key exchange without sharing private key |
| Common Algorithms | AES, DES | RSA, ECC |
| Key Size | 128–256 bits | 2048 bits or more |
| Typical Use | Bulk data encryption | Secure exchanges and signatures |
4. Deep dive: Security, strengths, and limitations
Both symmetric and asymmetric encryption methods offer unique benefits and face specific limitations. In this section, we’ll explore their strengths and weaknesses in detail, along with the risks they face and how those can be mitigated.

4.1 Strengths of symmetric encryption
Symmetric encryption is fast and uses less computing power. It works well when encrypting large amounts of data and is easier to implement, making it ideal for many everyday security needs.
4.2 Weaknesses of symmetric encryption
Its main drawback is the risk when sharing keys if the secret key leaks, anyone can access the data. Additionally, it lacks built-in authentication and is less secure in open or untrusted environments.
4.3 Strengths of asymmetric encryption
Asymmetric encryption allows safe key sharing since only the public key is distributed openly. It supports digital signatures to confirm authenticity and eliminates the need for pre-shared keys, making it ideal for secure communication over the internet.
4.4 Weaknesses of asymmetric encryption
This type requires more computing power and is slower, especially for large files. It also uses larger key sizes to maintain strong security standards.
4.5 Unique security risks and mitigations
Both encryption types face specific risks. Symmetric encryption’s key exchange can be vulnerable to interception attacks, while asymmetric encryption may be threatened by future quantum computing. To reduce risks, organizations follow standards like NIST guidelines and implement practices such as hybrid encryption protocols, regular key updates, and strong authentication measures.
Understanding the difference between symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption also helps identify where each method is more vulnerable to specific threats.
- Use secure channels or key exchange protocols
- Combine symmetric and asymmetric methods for balance
- Adopt post-quantum cryptography as it evolves
5. Use cases and practical guidance: When to use each encryption type
Let’s look at the ideal scenarios for using each encryption method, including hybrid approaches that combine both.

5.1 Symmetric: Best-fit scenarios
Symmetric encryption is best for situations needing fast, large-scale data protection. Ideal examples include:
- Encrypting large files or whole drives
- Protecting databases
- Securing live data streams, VPNs, and encrypted video sessions
5.2 Asymmetric: Best-fit scenarios
Asymmetric encryption fits where secure communication and identity verification are critical. Common uses are:
- Exchanging secret keys over unsecured networks
- Issuing digital certificates and authentication
- Proving sender identity with digital signatures
These use cases highlight one of the clearest manifestations of the difference between symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption in everyday applications.
5.3 Hybrid approaches and modern protocols
Many modern systems combine both methods, making it even more important to understand the difference between symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption to appreciate hybrid encryption protocols.
For example, SSL/TLS starts with asymmetric encryption to securely exchange keys. Then, it switches to symmetric encryption for faster bulk data handling. Messaging apps often use similar methods to keep chats private and efficient.
- SSL/TLS handshake: asymmetric key exchange followed by symmetric session keys
- Secure messaging protocols combining both to protect content and identities
SSL/TLS uses this hybrid model, as do platforms that allow users to buy and sell bitcoins securely while ensuring fast data handling.
6. Analogies and plain-English explanations
6.1 Symmetric encryption analogy
Think of symmetric encryption like a locked box with one key. Both the sender and receiver have the same key to lock and unlock the box. If someone else gets this key, your secret is exposed.
6.2 Asymmetric encryption analogy
Asymmetric encryption is like a public mailbox: anyone can drop a letter in (using the public key), but only the owner has the key to open and read the mail (private key).
6.3 Step-by-step example scenario
- Alice wants to send Bob a private email.
- She uses Bob’s public key to encrypt the message.
- The encrypted message travels safely over the internet.
- Bob uses his private key to decrypt and read the email.
This example demonstrates the core difference between symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption one requires a shared key, the other does not.
Related reads to deepen your knowledge:
7. Summary table and key takeaways
- Symmetric encryption uses one shared key; asymmetric uses two keys (public/private).
- Symmetric is faster and better for large data; asymmetric is slower but safer for exchanging keys.
- Symmetric’s main risk is key sharing; asymmetric supports secure key exchange and digital signatures.
- Common symmetric algorithms: AES; asymmetric: RSA and ECC.
- Hybrid protocols combine both for practical security and efficiency.
Especially if you’re planning to invest. See how can i invest in bitcoin.
The summary below reinforces the main difference between symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption for quick reference.
| Feature | Symmetric Encryption | Asymmetric Encryption |
|---|---|---|
| Keys | 1 shared key | Public/private pair |
| Speed | Fast | Slower |
| Security | Depends on key secrecy | Strong key exchange |
| Use | Large data encryption | Secure communication and authentication |
8. Frequently asked questions
8.1 Can you convert between symmetric and asymmetric encryption?
No, they are based on different mathematical principles and keys. However, both can work together in systems like SSL/TLS for best results.
8.2 Is one always more secure than the other?
Not necessarily. Symmetric encryption is secure for bulk data but risks key sharing. Asymmetric encryption is safer for key exchange but slower. Their security depends on use case and implementation.
8.3 How do key lengths impact security?
Longer keys generally mean stronger security. Symmetric keys use 128–256 bits, while asymmetric keys are much longer, typically 2048 bits or more, to resist attacks.
8.4 Do modern protocols use both?
Yes. Many modern systems combine symmetric and asymmetric encryption to balance speed and security, starting with asymmetric to exchange keys, then using symmetric for data transfer.
8.5 Why is understanding the difference between symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption important?
Because each method has different strengths, knowing their differences helps you apply the right encryption in the right context balancing speed, scalability, and security.
9. Conclusion
Understanding the difference between symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption is essential for protecting your digital assets. Each method serves distinct purposes: symmetric encryption excels in speed and volume, while asymmetric encryption ensures secure exchanges and authentication.
Here’s a quick recap:
- Symmetric = one key, fast, efficient for large data.
- Asymmetric = key pair, slower, best for secure key sharing.
- Modern systems often combine both for balanced protection.
- Key size and context matter: match the encryption type to your use case.
Choosing the right approach will help you avoid risks and improve your data protection strategy. Don’t forget to follow the Trader & Trading category on Vietnam-UStrade to stay up to date with the latest insights.
Which encryption method do you currently use or plan to use for your online activities?
We hope this guide helps you strengthen your digital defenses. Feel free to leave a comment or question below, or check out our latest posts in the cybersecurity category!