What is a Bitcoin mine, and why should beginners care in 2025? As Bitcoin continues to gain mainstream attention, the process behind how new coins are created known as mining remains one of the most misunderstood aspects of the crypto world.
Whether you’re new to digital assets or just curious about how Bitcoin operates behind the scenes, understanding what a Bitcoin mine is can give you valuable insights into the backbone of this decentralized network.
In this guide by Viet Nam – US Trade, we’ll break down Bitcoin mining in simple terms, explore how it works, what miners actually do, and why it still matters today.
1. What is a bitcoin mine?
For many newcomers to the world of cryptocurrencies, the term “Bitcoin mine” may sound confusing especially since it has little to do with traditional mining involving shovels and hard hats.
In reality, a Bitcoin mine is a digital infrastructure that plays a crucial role in maintaining the Bitcoin network and minting new coins. If you’ve ever wondered how Bitcoin is created or why mining exists in the first place, you’re in the right place.
This section provides a clear and beginner-friendly explanation of what a Bitcoin mine is, how it fits into the broader ecosystem, and why it’s essential to the functioning of the Bitcoin blockchain.
A Bitcoin mine refers to either:
- A physical location filled with specialized computers (called miners or mining rigs) dedicated to validating Bitcoin transactions, or
- The entire process of solving complex mathematical problems to secure the Bitcoin network and receive rewards in return.

This is where understanding what is a bitcoin miner becomes essential. A bitcoin miner is the specialized hardware or the person operating it that performs the core functions of mining: validating transactions and maintaining the integrity of the network.
Think of a Bitcoin mine as a data center specifically designed to support the blockchain. These centers can range from small setups in someone’s garage to massive facilities consuming megawatts of electricity.
Let’s break down the core features that define a Bitcoin mining operation:
| Feature | Description |
| Purpose | To ensure the authenticity of transactions and maintain the security of the blockchain |
| Equipment | Cryptocurrency mining machines built with application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) |
| Energy Usage | High, due to constant computational activity |
| Location | Can be anywhere with cheap electricity and stable internet |
| Reward System | Miners are compensated with newly minted Bitcoin and transaction fees |
Before we go further, let’s clear up two common misunderstandings:
- It’s not about digging: Bitcoin mining is purely digital there’s no physical coin to be found underground.
- Anyone can mine (technically): While technically true, profitability and scalability require serious investment and expertise.
2. What does it mean to mine a bitcoin?
When people say that “a Bitcoin is mined,” it often raises eyebrows how can a digital currency be mined at all? The phrase might sound metaphorical, but it actually describes a highly technical process that keeps the Bitcoin network running smoothly.
In this section, we’ll explore what it really means to mine a Bitcoin, how the process works behind the scenes, and why it’s crucial to the entire crypto ecosystem.
2.1. The core idea: bitcoin mining explained simply
At its core, Bitcoin mining is the process of adding new blocks to the Bitcoin blockchain a public digital ledger that records every transaction made with Bitcoin.
To add a new block, miners compete to solve a cryptographic puzzle. The miner who cracks the puzzle first earns the opportunity to:
- Confirm a group of transactions (called a block),
- Add that block to the blockchain, and
- Earn a reward in the form of newly minted Bitcoin and transaction fees.
This method of competition is referred to as the proof-of-work (PoW) mechanism.
In short: Mining is how new Bitcoins are created, and how the network reaches consensus without needing a central authority.

2.2. What occurs during the process of mining a bitcoin?
Here’s a breakdown of what actually happens when a new Bitcoin is mined:
- Miners collect transactions and organize them into a single block.
- Miners compete to solve a puzzle by generating “hashes” (random guesses).
- The first miner to find a valid hash announces the result to the network.
- Once confirmed, the block is incorporated into the blockchain ledger.
- The miner receives a block reward currently 3.125 BTC (as of the 2024 halving).
- This process repeats every ~10 minutes, 24/7.

2.3. Mining and scarcity
One of the key reasons Bitcoin is often called digital gold is because of its limited supply. The total supply of Bitcoin is capped at 21 million coins. This scarcity is enforced by the mining process:
- New Bitcoins are created as rewards, but the reward halves approximately every four years (a process called halving).
- Over time, mining becomes harder and less rewarding ensuring scarcity.
3. How does a bitcoin mine work in practice?
Understanding how a Bitcoin mine works in practice helps demystify the entire process of mining. While it may sound like something that happens deep in cyberspace, Bitcoin mining requires physical infrastructure, hardware, electricity, and sophisticated software.
In this section, we’ll walk through what a Bitcoin mining operation actually looks like in the real world whether it’s a small setup at home or a large-scale commercial mine.
A Bitcoin mine is not a physical cave or tunnel, but rather a facility where specialized computers (called miners or mining rigs) solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions on the Bitcoin network.
- These facilities can range from a single machine in a home office to massive data centers filled with thousands of mining rigs.
- A mine is equipped with hardware, cooling systems, power supplies, and internet connectivity.
- All mining operations compete globally to earn block rewards and transaction fees.
Think of a Bitcoin mine as a high-performance computing center dedicated to maintaining the Bitcoin blockchain and getting paid in Bitcoin to do so.
Here are the essential components that make a Bitcoin mine work:
| Component | Description |
| Mining Rigs (ASICs) | Specialized machines designed specifically to mine Bitcoin. Well-known examples are devices from the Antminer S19 lineup. |
| Power Supply Units | High-wattage units that feed electricity to mining rigs. The primary expense in operations comes from electricity consumption. |
| Cooling Systems | Mining equipment generates a significant amount of heat. Fans, ventilation, or even immersion cooling is used. |
| Mining Software | Programs like CGMiner or NiceHash that connect rigs to the Bitcoin network or mining pools. |
| Mining Pool Access | Most miners join pools to combine their hash power and share rewards more consistently. |
| Stable Internet | A fast and reliable internet connection is essential for staying connected to the Bitcoin network. |

Bitcoin Mine Example: Solo vs. Industrial:
- Solo miners might run one or two ASICs at home, often as a hobby or educational tool. Profitability is extremely low without scale.
- Commercial mining farms may house thousands of ASICs in a warehouse-like setting and operate around the clock. These require millions of dollars in investment.
4. What exactly is a bitcoin miner doing all day?
To truly understand Bitcoin mining, it’s important to break down the role of a Bitcoin miner. Despite the term, miners aren’t digging for digital gold with pickaxes. Instead, they’re operating machines that perform highly specialized tasks maintaining the integrity of the Bitcoin network and competing to earn rewards.
So, what is a bitcoin miner really doing throughout the day?
3.1. Mining: More than just solving puzzles
At its core, Bitcoin mining is about processing transactions and securing the network. The puzzle-solving part is just one piece of a broader mission. Here’s a breakdown of what miners actually do:
- Collect transactions from the Bitcoin mempool (a waiting area for unconfirmed transactions).
- Verify and validate each transaction based on Bitcoin’s rules.
- Group transactions into a new “block”.
- Hash the block using the SHA-256 algorithm, trying millions of combinations per second.
- Compete with other miners to find a hash value that meets Bitcoin’s current difficulty target.
- Broadcast the new block to the network once a valid hash is found.
- Earn block rewards (newly minted Bitcoin + transaction fees) if successful.
The miner who finds a valid block first gets the reward this is why mining is often compared to a lottery.

3.2. A typical day for a bitcoin miner
Here’s what a typical day might involve for different types of miners:
| Miner Type | Daily Activities |
| Solo Miner | Monitoring ASICs, checking mining software, power costs, and occasional reboots or updates. |
| Farm Operator | Managing hundreds or thousands of rigs, cooling infrastructure, technicians, network stability, firmware upgrades. |
| Pool Participant | Ensures uptime, optimizes efficiency, and monitors earnings from pool contributions. |
While much of the process is automated, profitability is a constant concern. Miners monitor:
- Bitcoin price and volatility
- Network difficulty adjustments (every 2,016 blocks)
- Electricity prices
- Hardware performance (hashrate, temperature, uptime)
Being a successful miner in 2025 means more than just plugging in a machine it requires strategy, optimization, and risk management.
4. How does a bitcoin lottery miner work?
Before diving into what a Bitcoin lottery miner is, let’s clarify something: this is not a separate category of miner or a different technology. Instead, the term “lottery miner” refers to the lottery-like nature of how Bitcoin mining works in practice.
This analogy helps newcomers understand why mining is both competitive and unpredictable, especially for solo participants.
See more related articles:
4.1. Why bitcoin mining is often called a lottery
Bitcoin’s Proof-of-Work system is designed to be a fair but random competition. Here’s how it’s similar to a lottery:
- Every miner is racing to find a valid hash for the next block.
- The chances of winning depend on how much computational power (hashrate) you contribute.
- Even if you do everything right, there’s no guarantee you’ll win.
- The “winner” earns the full block reward, just like a lottery jackpot.
So when people refer to a Bitcoin lottery miner, they usually mean:
❝A solo miner or small-scale operator hoping to win block rewards by chance, despite having limited computational power.❞

4.2. Bitcoin lottery miner vs. mining pool
Let’s break down the key differences between being a lottery miner and joining a pool:
| Feature | Bitcoin Lottery Miner (Solo) | Mining Pool Participant |
| Reward structure | All-or-nothing | Shared among contributors |
| Predictability of income | Very low | More stable and frequent |
| Required hardware | Usually high-performance | Can vary depending on pool |
| Risk of zero reward | High | Low |
| Best for | Risk-tolerant hobbyists | Consistent income seekers |
In 2025, due to rising difficulty and halving rewards, most miners join pools instead of going solo.
4.3. Should you try solo “lottery” mining?
While solo mining offers the thrill of potentially hitting a “jackpot,” it’s increasingly impractical without access to:
- Ultra-efficient mining rigs
- Very low-cost electricity
- Stable infrastructure
Unless you’re experimenting or have access to subsidized power, joining a reputable Bitcoin mining pool is the more realistic path to earning mining income in 2025.

5. How mining rewards work (and why they keep shrinking)
To truly understand the incentives behind Bitcoin mining, it’s important to grasp how miners get paid and why those rewards have been decreasing over time. This section will cover the structure of mining rewards, the Bitcoin halving event, and what it means for miners in 2025 and beyond.
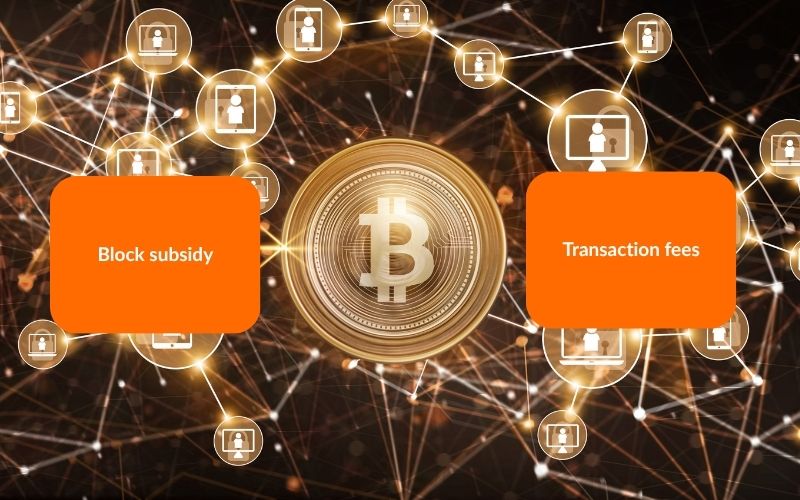
5.1. The two components of a mining reward
When a miner successfully adds a new block to the Bitcoin blockchain, they receive a reward made up of two parts:
- Block subsidy: This is the fixed number of new bitcoins generated with each block. It started at 50 BTC in 2009.
- Transaction fees: These are small fees users attach to their Bitcoin transactions. The miner who wins the block collects all the fees from the transactions included.
Example in 2025:
As of the most recent halving in April 2024, the block subsidy is now 3.125 BTC, down from 6.25 BTC.

5.2. Bitcoin halving: why rewards shrink every 4 years
The term Bitcoin halving refers to a scheduled event that occurs every 210,000 blocks (roughly every 4 years). When it happens:
- The reward for mining a block is reduced by 50%.
- The total number of new bitcoins entering circulation decreases.
- This continues until the maximum supply of 21 million BTC is reached (expected around the year 2140).
| Year | Block Reward | Event |
| 2009 | 50 BTC | Bitcoin launch |
| 2012 | 25 BTC | First halving |
| 2016 | 12.5 BTC | Second halving |
| 2020 | 6.25 BTC | Third halving |
| 2024 | 3.125 BTC | Fourth halving |
| ~2028 | 1.5625 BTC | Next halving |
This predictable deflationary model is a core part of Bitcoin’s value proposition: scarcity.

5.3. Why it matters for miners in 2025
In 2025, miners face a tighter reward environment:
- Lower block subsidy means less income per block.
- Transaction fees are expected to play a more significant role over time.
- Only the most efficient operations (low-cost power, optimized rigs) remain profitable.
Mining in 2025 is no longer just about power it’s about economics.
Read more: What Happens When Bitcoin Halves? Explained Simply
6. Can you still start bitcoin mining in 2025?
With rising competition, shrinking rewards, and increasing electricity costs, many newcomers wonder: Is it too late to start mining Bitcoin in 2025? The answer depends on your goals, resources, and understanding of the mining landscape today.
6.1. It’s still possible but no longer for everyone
Bitcoin mining is not as accessible as it was in the early 2010s. Back then, anyone with a decent laptop could mine from home. In 2025, however, mining is:
- Highly competitive: Large-scale operations dominate the space.
- Capital-intensive: Requires significant investment in hardware and electricity.
- Location-dependent: Miners seek regions with ultra-low power costs, such as hydro-rich zones in Canada or Iceland.

If you’re an individual looking to get started, you typically have two options.
6.2. Two main ways to start bitcoin mining today
- Home mining (still possible, but rarely profitable)
Some hobbyists still run ASIC miners (specialized machines) at home, but face challenges:
- High power bills
- Noise and heat issues
- Difficult to break even in most regions

Best suited for tech-savvy enthusiasts with access to cheap power.
- Cloud mining or hosted mining
Cloud mining services let you rent mining power from large farms. You pay an upfront fee and share in the profits (or losses). Hosted mining means you buy the hardware but someone else operates and maintains it for you.
Be cautious: Many cloud mining schemes have turned out to be scams. Only work with transparent, regulated providers.
| Method | Pros | Cons |
| Home Mining | Full control, hobby-friendly | High costs, low ROI, noisy |
| Cloud Mining | No setup required | Potential for fraud and lack of full transparency |
| Hosted Mining | Efficient, less maintenance | Upfront investment, trust required |
Key points to evaluate before beginning
Before getting started, consider asking yourself:
- How much does electricity cost where I live?
- Can I access modern, efficient ASIC miners (e.g., Antminer S21)?
- Am I comfortable with the risk vs. reward ratio?
If your answer is “yes” to these and you’re willing to operate at scale mining might still be viable in 2025.
7. How bitcoin mining keeps the network safe
At first glance, Bitcoin mining might look like a way to earn free crypto. But beneath the surface, mining plays a critical role in protecting the Bitcoin network by ensuring that transactions are valid and the system remains decentralized and secure.
7.1. Mining as a security backbone
Every 10 minutes, miners race to solve a complex mathematical puzzle. The successful miner earns the right to append a new block of transactions to the blockchain. This process, known as Proof of Work (PoW), serves two vital security purposes:
- Validates transactions: Only verified transactions are included in blocks.
- Prevents double spending: The consensus mechanism makes it practically impossible for someone to spend the same bitcoin twice.
7.2. Why attacking bitcoin is nearly impossible
Bitcoin’s network is decentralized, with miners operating across the globe. To successfully attack the network (e.g., rewrite the blockchain), a hacker would need to control over 51% of the total mining power a feat that’s:
- Technically challenging
- Extremely expensive
- Easily detected and countered

This is why large-scale mining contributes to Bitcoin’s resilience: the more miners, the harder it is to compromise the system.
Read more: How Safe Is Bitcoin? A Complete Explanation and How to Invest Safely in Bitcoin
7.3. Proof of work vs. other consensus models
Other cryptocurrencies, such as Ethereum (post-Merge), have shifted to Proof of Stake (PoS). While PoS consumes less energy, PoW still offers unmatched transparency and auditability in Bitcoin.
| Feature | Proof of Work (Bitcoin) | Proof of Stake (Ethereum, etc.) |
| Energy Use | High | Low |
| Hardware Requirement | ASIC miners | Just cryptocurrency for staking |
| Security Strength | Proven, battle-tested | Still evolving |
| Censorship Resistance | Very strong | Changes based on the specific implementation |
7.4. Mining helps enforce bitcoin’s monetary policy
Beyond security, mining also enforces Bitcoin’s supply schedule. Since miners receive newly minted bitcoin as block rewards, the code ensures that no more than 21 million bitcoins will ever exist making Bitcoin scarce by design.
8. Bitcoin mining vs other crypto models
As the crypto landscape evolves, Bitcoin’s mining-based model is often compared to newer alternatives like staking or delegated consensus. To understand why Bitcoin still sticks with mining, we need to explore the key differences between mining and other crypto validation systems.
8.1. Different ways to secure a blockchain
Cryptocurrencies use various consensus mechanisms to validate transactions and secure their networks. Here’s how Bitcoin mining compares with the most common alternatives:
| Consensus Mechanism | Example Coins | How It Works | Energy Use | Decentralization Risk |
| Proof of Work (PoW) | Bitcoin, Litecoin | Miners solve math puzzles to add blocks | High | Low (widely distributed) |
| Proof of Stake (PoS) | Ethereum, Cardano | Validators stake coins and are chosen to create blocks | Low | Medium (rich get richer) |
| Delegated PoS (DPoS) | EOS, Tron | Small group of elected validators control the chain | Very Low | High (centralized control) |
| Proof of Authority (PoA) | VeChain, BNB Smart Chain | Authority nodes create blocks | Very Low | Very High (trusted parties) |
8.2. Why bitcoin still uses mining (pow)
Bitcoin remains committed to Proof of Work because of its transparency, security, and long-term reliability. Unlike newer models, PoW:
- Doesn’t rely on “trust” or reputation.
- Keeps power distributed among miners.
- Has been proven to withstand attacks for over a decade.

8.3. The energy debate (and bitcoin’s answer)
Bitcoin mining is often criticized for its energy consumption, but it’s essential to put this in context:
- A large portion of mining now uses renewable energy.
- Energy use supports economic incentives for security.
- Alternative systems may use less power, but sacrifice other principles like decentralization or immutability.
According to the Bitcoin Mining Council, over 50% of the network now uses sustainable power sources.
8.5. Use case drives the model
Each blockchain is designed for a different purpose. Bitcoin’s mission to be a decentralized store of value means it prioritizes security and trustlessness which is exactly what Proof of Work delivers.
9. Final thoughts: Why bitcoin mining still matters in 2025
Even after more than a decade, Bitcoin mining remains the backbone of the world’s largest cryptocurrency. While new consensus models like Proof of Stake gain popularity, mining still holds a crucial role both technically and ideologically in the crypto ecosystem.
As of 2025, Bitcoin mining is far more than just a way to earn BTC. It is:
- A security layer: Mining provides a defense mechanism against fraud and double-spending.
- A transparency tool: Anyone can verify transactions via mining’s open-source rules.
- A symbol of decentralization: Mining power is distributed globally, reducing reliance on any central entity.
- A gateway for participation: For those with the right resources, mining still offers a direct way to support the Bitcoin network and earn rewards.
The bigger Picture: Bitcoin’s continued use of Proof of Work is not due to technological stagnation it’s a conscious decision to prioritize security, fairness, and censorship resistance. In a world increasingly digital and centralized, Bitcoin mining stands as a rare model of trustless infrastructure.
If you’re considering entering the mining space:
- Research hardware ROI carefully (ASICs vs GPUs).
- Check electricity costs and local regulations.
- Explore mining pools or cloud mining options.
- Stay updated on Bitcoin halving and reward changes.
In the end, understanding what is a Bitcoin mine is more than grasping how blocks are added or rewards are earned it’s about appreciating the foundation of a decentralized future.
At Viet Nam – US Trade, our mission is to help you navigate this landscape with clarity, whether you’re a curious beginner or a seasoned investor. With transparent, expert-backed insights, we empower you to make informed decisions no hype, no pressure, just knowledge.
Want to explore more ways to participate in crypto securely? Check out our Beginner’s Guide to Bitcoin or compare trusted crypto platforms.






