Ever wondered what is bitcoin blockchain, or what technology stands behind it? We’re here to help you understand just that. Let’s explore what is Bitcoin blockchain it’s essentially a massive, super-secure, and totally transparent digital ledger. Thanks to it, every Bitcoin transaction happens smoothly and quickly, without anyone in the middle controlling it. If you’re ready to uncover the secret behind the world’s most popular digital currency, this is the perfect place to start!
1.What is Blockchain?
Bitcoin’s blockchain is a decentralized, distributed digital ledger that continuously stores a growing list of records, known as blocks. These blocks are securely linked together using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data.
In essence, Bitcoin’s blockchain operates as a secure and transparent system that records transactions across a network of computers. This structure ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered retroactively without modifying all subsequent blocks and obtaining consensus from the entire network. This makes Bitcoin’s blockchain an innovative and trustworthy solution for verifying digital transactions without the need for a central authority.
Unlike traditional databases managed by a central authority, blockchain stores data across multiple nodes (computers) in a peer-to-peer network. Every transaction is validated through a consensus mechanism such as proof of work or proof of stake ensuring that all participants agree on the data’s accuracy before it’s added to the chain.
Each group of transactions is stored in a “block.” These blocks are cryptographically linked to one another, forming a continuous, unchangeable chain. This structure protects data integrity and makes blockchain ideal for high trust applications, including cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, smart contracts, and supply chain transparency.
One of blockchain’s biggest advantages is its ability to deliver security, transparency, and trust without the need for traditional intermediaries like banks or centralized institutions. This reduces the risk of fraud and human error while enhancing efficiency and accountability. As a result, blockchain is increasingly used in sectors that require reliable, real-time data, such as finance, healthcare, logistics, and legal industries.
Whether you’re a business leader exploring ways to streamline operations or a tech enthusiast curious about the future of digital innovation, understanding blockchain is a valuable step in navigating today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape.

1.1 What Is a Block in the Bitcoin Blockchain?
To truly understand what is bitcoins blockchain, it’s important to first know what a block is — because the blockchain is made up of these blocks.
A block is a digital container that stores a group of Bitcoin transactions. Think of it as a “page” in a ledger, where each page records recent transactions made on the Bitcoin network. These blocks are linked together in a strict, chronological order to form the blockchain a continuous chain of transaction records.
Each block is connected to the one before it by a unique identifier known as a cryptographic hash. This hash acts like a fingerprint, helping to maintain the integrity and order of the chain. It ensures that the blocks are secure, tamper-proof, and verifiable. If someone tries to alter a past block, the entire chain becomes invalid, which is why the blockchain is considered immutable.
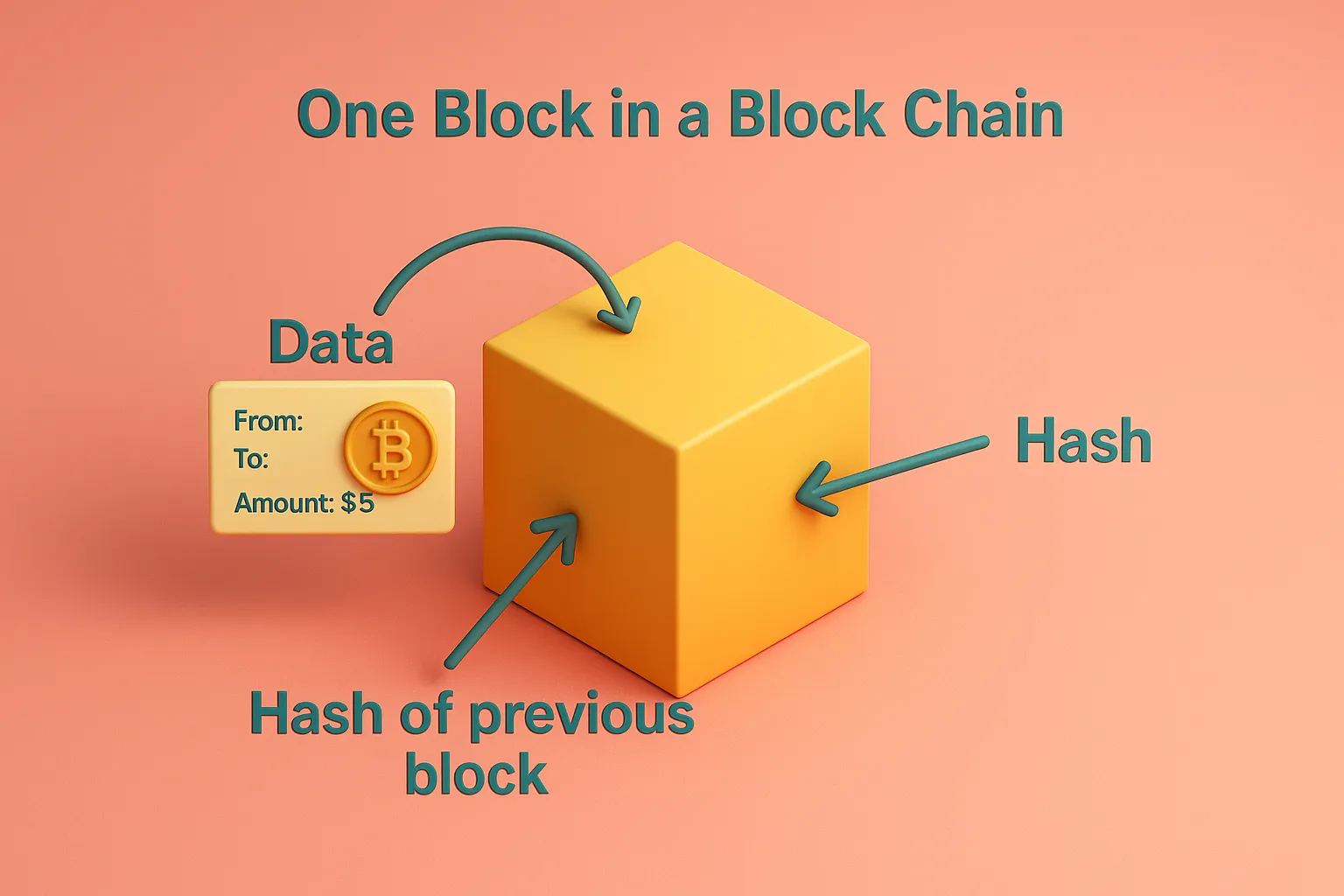
A new block is created roughly every 10 minutes through a process called Bitcoin mining. Bitcoin miners harness high powered computers to crack complex cryptographic puzzles. When they successfully solve a puzzle, they validate a new block and add it to the blockchain. As a reward for securing the network and confirming transactions, miners receive newly minted Bitcoins.
Once a block is completed and added to the blockchain, it becomes a permanent part of the ledger. It cannot be changed or deleted, though it can be copied for record keeping. This process is crucial in keeping the Bitcoin blockchain secure, transparent, and decentralized.

2.How is the Bitcoin Blockchain different from other Blockchains?
When people ask what is Bitcoin blockchain, they often confuse it with other types of blockchains. While all blockchains are decentralized and tamper resistant, they serve different purposes. Here’s how Bitcoin compares to Ethereum, Solana, and private blockchains:
Bitcoin: Built for Digital Payments
The Bitcoin blockchain is designed for secure, peer-to-peer digital currency transactions. It’s simple, highly secure, and optimized for transferring Bitcoin not for running apps or complex logic.
Ethereum: Smart Contracts & Web3
Ethereum expands blockchain use by supporting smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). It powers the Web3 ecosystem, including NFTs, DeFi, and DAOs.
Solana: High-Speed Blockchain
Solana focuses on fast, low-cost transactions. With its unique Proof of History consensus, it’s ideal for real-time apps like gaming and micro payments.
Private Blockchains: Enterprise-Ready
Platforms like Hyperledger are used by businesses. These blockchains are permissioned, offering greater control and privacy for use cases like supply chain tracking or internal audits.
The key differences between the Bitcoin blockchain and other blockchain platforms
3. How Bitcoin Blockchain works
To truly understand what is Bitcoin blockchain, it’s important to explore how this technology functions and why it has become such a foundational part of modern digital finance. At its core, the Bitcoin blockchain is a decentralized and public digital ledger that records every transaction made using Bitcoin. What makes it revolutionary is that it doesn’t rely on banks or central authorities to verify or store these transactions. Instead, the power is distributed among participants in the network, making the entire system transparent, secure, and self-sustaining for how the Bitcoin blockchain works
Before the advent of Bitcoin, the concept of digital money had always required a trusted third party to keep records and prevent double-spending. Whether it was a bank or a payment provider, there had to be someone to manage the ledger essentially the record book of who owns how much. Bitcoin changed this model entirely. In the Bitcoin blockchain, every participant has access to the same copy of the ledger, and once a transaction is confirmed, it becomes part of a permanent and unchangeable history. This is why Bitcoin is often described as “trustless” because trust is no longer placed in any one entity, but in the system itself.
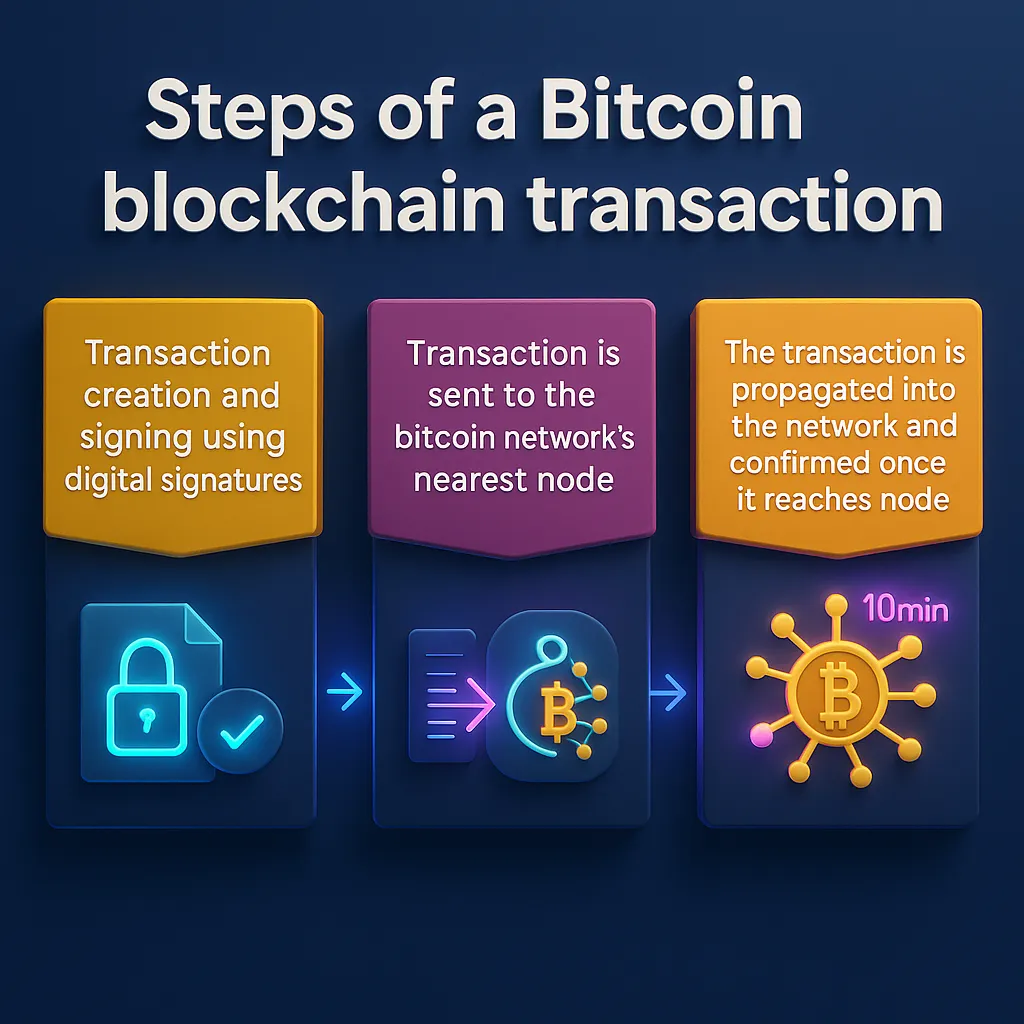
All Bitcoin transactions are recorded on the Bitcoin blockchain, a global network where mining and hashing take place. Mining is how transactions are verified and permanently recorded on the blockchain. This involves using hashing power, which refers to the computational effort required to solve complex mathematical problems. When a miner successfully solves one of these problems, a new block containing a group of verified transactions is added to the chain, and the miner is rewarded with newly created Bitcoin.
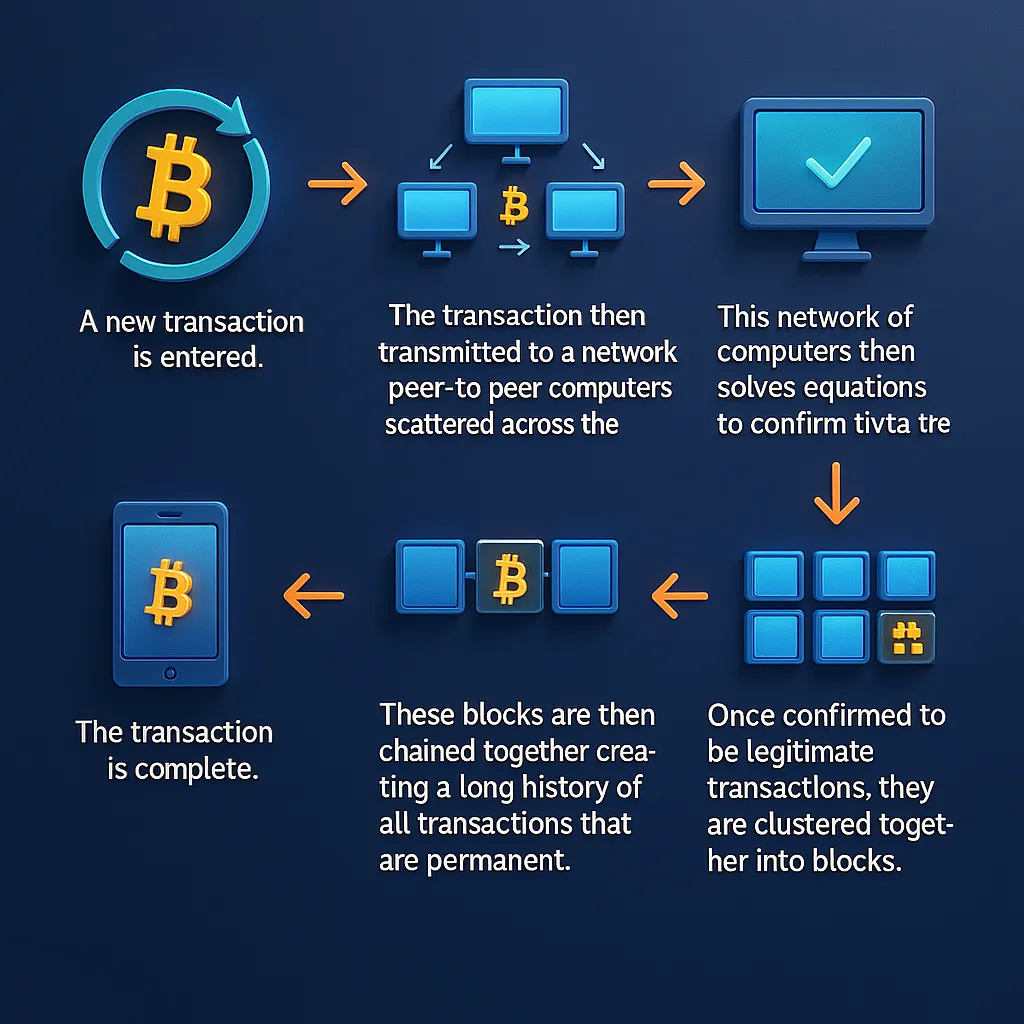
Most Bitcoin users don’t mine coins themselves. Instead, they acquire Bitcoin through cryptocurrency exchanges, platforms that allow users to buy, sell, and trade Bitcoin and other digital assets. Behind the scenes, however, the blockchain is operating continuously processing transactions, validating data, and maintaining a complete and synchronized record across the entire network. Every user, miner, and node contributes to this process in some way, forming a decentralized infrastructure with no single point of control.
Technically speaking, is a type of database, but it functions very differently from traditional databases. In a regular database, information is typically stored in tables that can be edited or deleted. By contrast, blockchain stores data in blocks groups of information with a fixed capacity. Once a block is full, it is linked to the previous one using a cryptographic hash, a unique code that secures the data and links it immutably to the what is bitcoin blockchain
This structure is what makes blockchain so secure. Every block contains a hash of the previous block, creating a connected chain of data that cannot be changed retroactively without altering every single block that follows. This makes tampering with the blockchain virtually impossible, especially since the data is also distributed across thousands of independent computers, known as nodes, all working to keep the network honest.
Within this system, miners play a crucial role. These are specialized machines that dedicate their processing power to verifying transactions and creating new blocks. When a miner solves a complex algorithm and adds a block to the chain, they are rewarded with Bitcoin. This incentive system ensures that participants continue to invest resources into maintaining the blockchain’s security and reliability.
In contrast to centralized databases, where information can be quickly updated or modified by administrators, blockchain is immutable once data is written, it cannot be changed. Each block is timestamped, creating a transparent timeline of activity that anyone can audit. This immutability is a key reason why blockchain is trusted for recording financial transactions and has inspired use cases far beyond cryptocurrency, including supply chain tracking, identity verification, and digital contracts.
So, when we ask what is Bitcoin blockchain, we’re really asking about more than just ow the Bitcoin blockchain works. We’re talking about a breakthrough in how digital information is recorded, shared, and trusted. Bitcoin was the first rea world application of blockchain technology, and it demonstrated that it’s possible to create a decentralized financial system based entirely on code, mathematics, and consensus.
This innovation continues to shape the future of money and digital infrastructure. Whether you’re an investor, developer, or someone simply curious about new technology, understanding what is bitcoin blockchain is a key step in grasping how our digital economy is evolving and why decentralization, transparency, and security matter more than ever.
4. Understanding the pros and cons of Bitcoin Blockchain technology
What is bitcoin blockchain is a revolutionary technology that has transformed the way we think about digital transactions. Let’s explore its advantages and disadvantages to understand its impact better.
Key Advantages of the Bitcoin Blockchain
1. Immutability – Data That Can’t Be Altered
Data stored on the Bitcoin blockchain is permanent it can’t be changed or erased. This feature ensures that transaction histories are permanent and tamper proof, providing a reliable audit trail.
2. Transparency: Open and Verifiable
Every transaction on the Bitcoin blockchain is visible to all participants. Because the system is transparent, users can independently verify transactions building trust across the network.
3. Decentralization – Power to the Network, Not Institutions
Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network of computers (nodes), meaning no single entity controls the system. This makes the system less vulnerable to censorship and outside interference.
4. Traceability: Track Assets Efficiently
The blockchain records every transaction, allowing users to trace the origin and journey of assets. This is particularly useful in supply chains and for verifying the authenticity of goods.
5. Lower Transaction Fees: Cost-Effective Transfers
By eliminating intermediaries like banks, Bitcoin transactions often incur lower fees, making it an economical choice for transferring funds globally.
6. Enhanced Security: Robust Protection
Transactions on the Bitcoin blockchain are secured using cryptographic techniques, making it highly resistant to fraud and unauthorized access.
Disadvantages of Bitcoin Blockchain
1. High Implementation Costs
Setting up a Bitcoin blockchain system requires significant investment in infrastructure and technology, which can be a barrier for some organizations.
2. Performance Limitations
The Bitcoin network can process a limited number of transactions per second, leading to potential delays and scalability issues during high demand periods.
3. Data Immutability Challenges
While immutability is an advantage, it can also be a drawback when errors occur, as correcting mistakes on the blockchain is complex and costly.
4. High Energy Consumption
Bitcoin mining, the process of validating transactions, consumes a substantial amount of energy, raising environmental concerns.
5. Private Key Management
It’s up to users to keep their private keys safe and secure. Loss or theft of these keys can result in the irreversible loss of access to their Bitcoin holdings.
6. Potential for Illicit Activities
The pseudonymous nature of Bitcoin transactions can be exploited for illegal activities, posing challenges for law enforcement.

5. Advanced Security: How the Bitcoin Blockchain Stays Safe
Security is one of the most critical features that define what is Bitcoin blockchain. But how exactly does the network stay secure against fraud, tampering, or cyberattacks? Let’s break down the core security mechanisms that protect Bitcoin and keep it trustworthy for millions of users.
Consensus Mechanism: Proof of Work (PoW)
Bitcoin uses a process called Proof of Work, where miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles. This ensures that all transactions are verified and agreed upon by the network before being added to the blockchain. It’s an energy intensive process, but it makes the network incredibly hard to hack or manipulate.
What Is a 51% Attack?
A common concern in blockchain security is the 51% attack when a single entity gains control of more than half of the network’s mining power. In theory, this could allow them to double-spend coins or reverse transactions. However, in Bitcoin’s case, this is extremely unlikely due to the massive scale and decentralization of the network. Gaining that much control would require an astronomical amount of computing power and resources.
Why Bitcoin Is So Resilient
The Bitcoin blockchain’s security doesn’t rely on trust in people it relies on mathematics, cryptography, and game theory. Every block is cryptographically linked to the one before it, and tampering with any block would require re-mining the entire chain, which is virtually impossible due to the energy and time required.
Additionally, Bitcoin’s open source nature means developers and security experts around the world continuously audit the code and contribute to its improvement. This global transparency helps identify risks early and keeps the system honest.

In summary, part of understanding what is Bitcoin blockchain involves appreciating the robust security model it uses. From its consensus algorithm to its decentralized architecture, Bitcoin remains one of the most secure networks in the digital world trusted by individuals, institutions, and developers alike.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What is Bitcoin blockchain in simple terms?
The Bitcoin blockchain is a decentralized ledger that permanently records every Bitcoin transaction. It’s like a shared online spreadsheet that is secure, transparent, and cannot be altered. Every transaction is grouped into a “block” and linked to previous blocks, forming a continuous chain.
2. How does Bitcoin blockchain work?
Bitcoin blockchain works by using a network of computers (called nodes) that verify and record transactions. These transactions are grouped into blocks. Once verified through a process called mining, the blocks are added to the blockchain. This process ensures transparency, security, and eliminates the need for a central authority.
3. Why is the Bitcoin blockchain considered secure?
Bitcoin blockchain uses advanced cryptography and a consensus mechanism called Proof of Work (PoW) to ensure data integrity. Every block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, making it nearly impossible to alter past data without changing the entire chain which requires massive computing power.
4. Can Bitcoin blockchain be hacked?
While no system is entirely immune to risk, the Bitcoin blockchain is considered highly secure. A theoretical “51% attack” would require a single entity to control more than half of the network’s computing power, which is extremely difficult and expensive due to Bitcoin’s size and global distribution.
5. What makes Bitcoin different from other blockchains like Ethereum or Solana?
Bitcoin is designed primarily for secure, peer-to-peer digital payments. Ethereum supports smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps), while Solana focuses on high-speed and low-cost transactions. Each blockchain serves different use cases in the broader ecosystem.
6. What are the main advantages of using Bitcoin blockchain?
The key advantages include:
- Immutability: Data can’t be changed once recorded.
- Transparency: Transactions are visible to everyone.
- Decentralization: No central control or authority.
- Security: Advanced encryption protects against fraud.
- Lower Fees: Fewer intermediaries reduce transaction costs.
7. What are the downsides or limitations of Bitcoin blockchain?
Some notable disadvantages include:
- High energy consumption due to mining.
- Limited scalability (slow transaction speeds).
- High setup costs for businesses.
- Complex error correction due to immutability.
- Risk of losing private keys, which means loss of access to funds.
8. Why should I care about understanding Bitcoin blockchain?
6. Conclusion: What Is Bitcoin Blockchain and Why It Matters
Understanding what is Bitcoin blockchain means recognizing the core of a decentralized financial system that’s transforming our digital world. More than just the technology behind Bitcoin, the blockchain is a secure, transparent, and tamper proof ledger that allows peer-to-peer transactions without the need for banks or central authorities.
This guide has shown what is bitcoin blockchain in practice through mining, cryptographic hashes, and the validation of each block. Its key strengths lie in its immutability, transparency, and decentralization, though it still faces challenges like scalability, high energy usage, and regulatory pressures.
See more related articles:
- What do you do with Bitcoins? 6 profitable secrets you should know in 2025
- Who owns the most Bitcoins? Top holders 2025
- What is wrapped Bitcoin? Expert insights into wBTC explained
As innovation continues, the Bitcoin blockchain remains a driving force behind the evolution of digital finance. Whether you’re a developer, investor, or tech enthusiast, understanding this technology is crucial. So if you’ve ever wondered, “What is Bitcoin blockchain?”, now you know: it’s not just a buzzword it’s the secure backbone of the world’s most trusted cryptocurrency and a catalyst for change across multiple industries.
For more insights on the intersection of digital finance and global markets, check Bitcoin‘s out our resources on VN-US Trade to stay ahead in the evolving economy.





