Staking has become a popular way to earn rewards in the crypto world, prompting many to ask: Can you actually stake Bitcoin? If you’re wondering what Bitcoin staking is and whether it’s a viable option for the original cryptocurrency, you’re in the right place.
This guide will clarify the concept, explain Bitcoin’s underlying mechanics, and explore the alternative methods often referred to as ‘Bitcoin staking,’ helping you understand how you might generate yield on your BTC holdings.
1. Understanding Staking in the Cryptocurrency World
Before diving into the specifics of “Bitcoin staking,” it’s essential to grasp what staking generally means within the broader cryptocurrency landscape. This foundational knowledge will help clarify why the concept of what is Bitcoin staking isn’t as straightforward as it might seem for other digital assets.
1.1. What is Staking?
Staking is a way to earn rewards by locking up your cryptocurrency to participate in validating transactions and securing a blockchain network, especially those using a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) mechanism. In return for your commitment, you receive staking rewards, usually in the network’s native cryptocurrency.
1.2. Comparing Proof-of-Stake (PoS) and Proof-of-Work (PoW)
To fully understand staking, it’s vital to differentiate between the two primary consensus mechanisms blockchains use to validate transactions and create new blocks: Proof-of-Stake (PoS) and Proof-of-Work (PoW).
- Proof-of-Stake (PoS): This consensus mechanism allows individuals to validate block transactions based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” or lock up. Essentially, the more coins a participant stakes, the higher their probability of being chosen to validate a new block and earn the associated rewards.
PoS is often highlighted for its energy efficiency compared to PoW, as it doesn’t require vast computational power. Many newer cryptocurrencies and some established ones (like Ethereum after its Merge) use PoS, making direct staking a core feature. - Proof-of-Work (PoW): This is the original blockchain consensus mechanism, most famously employed by Bitcoin. PoW relies on “miners” who compete to solve complex cryptographic puzzles using powerful computer hardware.
The first miner to successfully solve the puzzle gets to add the next block of transactions to the blockchain and receives rewards in the form of newly minted coins and transaction fees. While PoW is known for its robustness and security, it is significantly more energy-intensive.
The critical distinction here is that traditional staking—the act of locking up coins to participate in network validation and earn staking rewards—is inherently tied to the Proof-of-Stake model. This fundamental difference is key when we later explore the question of what Bitcoin staking is.
2. Can you directly stake Bitcoin (BTC)?
Now that we’ve established a general understanding of staking and its connection to Proof-of-Stake, we can directly address the central question: Can you actually stake Bitcoin (BTC) in the traditional sense? Understanding Bitcoin’s fundamental design is key to answering this.
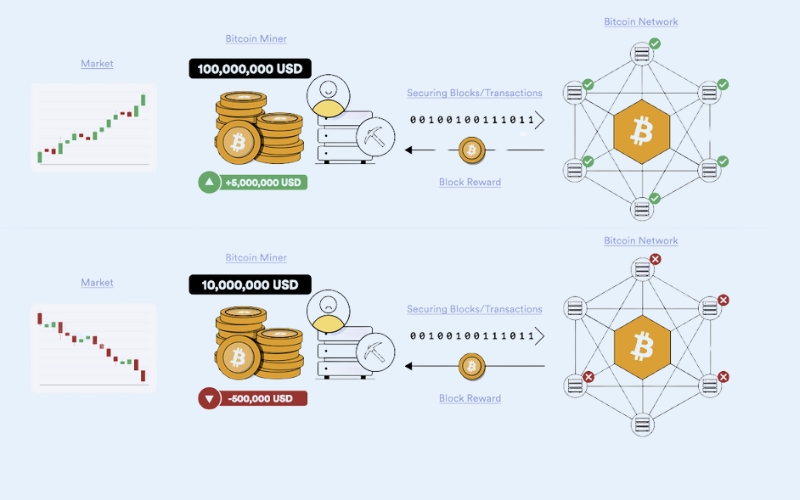
2.1. Bitcoin’s consensus mechanism: Proof-of-Work (PoW)
Bitcoin, as the pioneering cryptocurrency, operates on a consensus mechanism known as Proof-of-Work (PoW). This system is the bedrock of its security and how new transactions are verified and added to its public ledger, the blockchain.
In the PoW model, individuals or entities known as “miners” use specialized, high-powered computing hardware to solve complex mathematical problems. This process, commonly referred to as “mining,” is highly competitive.

The first miner to successfully solve the puzzle gets the right to validate a new block of transactions. For their effort and computational resources expended, these miners are rewarded with newly created Bitcoin (block rewards) and transaction fees paid by users. This mining process is how new Bitcoins enter circulation and how the network remains secure and decentralized.
2.2. Why native Bitcoin (BTC) cannot be staked directly
Given Bitcoin’s reliance on the Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism, the direct, native staking of BTC is not possible. The core protocol of Bitcoin does not include any functionality for users to “lock up” their BTC to participate in transaction validation and earn staking rewards in the way PoS coins do.
The concept of staking, as discussed earlier, is intrinsically linked to Proof-of-Stake networks. On these networks, holding and locking coins grants a user the chance to validate transactions. Bitcoin’s security and block creation rely on computational power (mining), not on the amount of BTC held or “staked” by participants.

Therefore, if you’re looking to engage in the traditional form of staking directly on the Bitcoin blockchain itself, the answer is a clear no. You cannot “stake” your BTC on the Bitcoin network to validate transactions and receive rewards in the same way one might stake Ethereum (ETH) on the Ethereum PoS network. This fundamental difference leads to the question: If direct staking isn’t an option, what is Bitcoin staking actually referring to when people use the term? We’ll explore that in the next section.
3. Types of staking Bitcoin
It’s crucial to understand that Bitcoin (BTC) itself, operating on a Proof-of-Work (PoW) network, cannot be “staked” in the same way as Proof-of-Stake (PoS) coins. Traditional staking involves participating in network consensus and validation.
However, the term “Bitcoin staking” is often informally used to describe various methods that allow BTC holders to earn a return or yield on their assets. These involve utilizing your Bitcoin in different financial products or platforms rather than direct blockchain staking. Here are the common types:
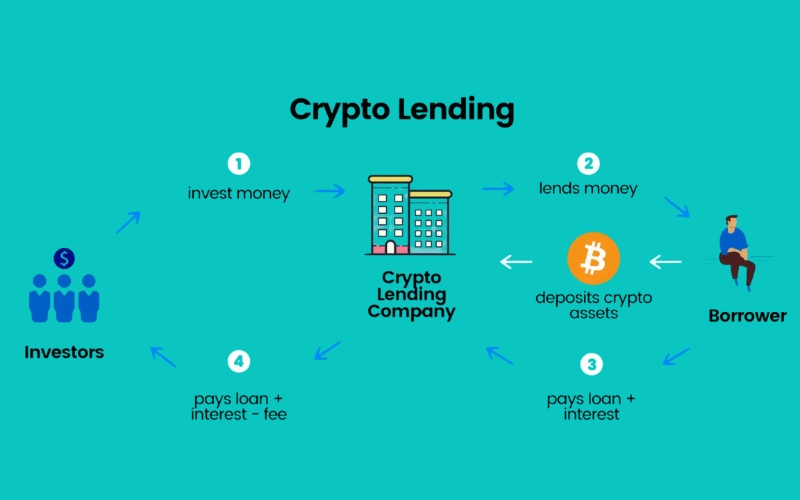
3.1. Bitcoin lending
This involves lending your Bitcoin to borrowers through centralized (CeFi) or decentralized (DeFi) platforms. In return for lending your BTC, you earn interest.
- CeFi Lending: You deposit BTC on platforms like Nexo, Ledn, or exchanges offering ‘earn’ products. These platforms lend it out and share interests with you. It’s generally user-friendly but involves counterparty risk as they hold your BTC.
- DeFi Lending: You supply BTC (often as Wrapped Bitcoin, wBTC) to decentralized protocols like Aave or Compound. Interest is earned algorithmically. This offers more transparency but involves smart contract risks and can be more complex.
3.2. Interest-bearing accounts on exchanges
Many major cryptocurrency exchanges (CEXs) offer “savings” or “earn” accounts where you can deposit your Bitcoin to earn interest.
How it works: You commit your BTC to these accounts for flexible or fixed terms. The exchange uses these funds (e.g., for lending) and pays you a predetermined interest rate, which is often higher for locked, fixed terms.
This is convenient if you already use the exchange, but it’s a custodial solution (the exchange holds your BTC), and rates can change.
3.3. Liquidity provision with Bitcoin in DeFi
You can earn rewards by providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges (DEXs), usually with Wrapped Bitcoin (wBTC) or other tokenized forms of Bitcoin.
How it works: You deposit an equal value of wBTC and another asset (e.g., ETH or a stablecoin) into a liquidity pool. You then earn a share of the trading fees generated by that pool and sometimes additional “yield farming” rewards.
This can offer potentially high returns but comes with risks like impermanent loss and smart contract vulnerabilities. It requires a good understanding of DeFi.
3.4. Using tokenized Bitcoin on other blockchains
This method involves “wrapping” your native Bitcoin to create a tokenized version (like wBTC on Ethereum) that can be used on other blockchains compatible with smart contracts and DeFi applications.
How it works: Once your BTC is tokenized, you can use this wBTC (or similar) in various DeFi protocols for lending, liquidity provision, or other yield-generating activities available on that specific blockchain.
This expands Bitcoin’s utility but introduces risks related to the wrapping mechanism (custodial risk for the bridge/custodian) and the smart contracts of the DeFi protocols you interact with.
Important Reminder: Always remember that any method offering a yield on your Bitcoin introduces new risks (counterparty, smart contract, market, etc.). Thorough research is essential before committing your BTC to any platform or protocol.
See more related articles:
- How Bitcoin Works for Beginners: A Simple Explanation for Everyone
- How to Earn Bitcoins? 11 Effective Ways for Beginners to Get Started
- How Safe Is Bitcoin? A Complete Explanation and How to Invest Safely in Bitcoin
4. If not direct staking, what do people mean by Bitcoin Staking?
Given that native Bitcoin (BTC) cannot be staked directly on its own Proof-of-Work blockchain, you might wonder why the term Bitcoin staking is so prevalent. Often, this phrase is used somewhat loosely to describe various alternative methods that allow Bitcoin holders to earn interest on Bitcoin or generate a yield from their assets, rather than true, protocol-level staking.
These methods don’t involve participating in Bitcoin’s network consensus directly but offer ways to put your BTC to work. Let’s explore some of the most common strategies that fall under this umbrella.
4.1. Alternative 1: Earning interest through Bitcoin Lending
One of the primary ways people generate returns on their Bitcoin is through Bitcoin lending. This involves lending your BTC to borrowers, who could be individuals or institutions, in exchange for interest payments over a set period.
This process is typically facilitated by centralized finance (CeFi) platforms (like cryptocurrency exchanges or dedicated lending services) or decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols. These platforms act as intermediaries, matching lenders with borrowers and managing the terms of the loan.

How it works: You deposit your Bitcoin onto a platform, which then lends it out. You receive interest, usually paid in Bitcoin or sometimes in other cryptocurrencies, based on the agreed-upon rate and term.
- Advantages: It can provide a relatively straightforward way to earn passive income from Bitcoin without needing specialized mining hardware. The interest rates can sometimes be attractive compared to traditional savings accounts.
- Disadvantages/Risks: The primary risk is counterparty risk – the platform you lend through could become insolvent or be subject to hacks. There’s also platform risk, where the platform itself might mismanage funds. Critically, when you lend your Bitcoin, you often relinquish direct control, embodying the crypto adage, “not your keys, not your coins.”
4.2. Alternative 2: Staking wrapped bitcoin (WBTC) and other BTC-pegged tokens
Another approach involves using “wrapped” versions of Bitcoin, with Wrapped Bitcoin (wBTC) being the most prominent example. Wrapped Bitcoin is an ERC-20 token on the Ethereum blockchain (or similar tokens on other Proof-of-Stake blockchains) that is pegged 1:1 to the value of Bitcoin.\

How it works: Real Bitcoin is locked up with a custodian, and an equivalent amount of wBTC is “minted” on the Ethereum network. This wBTC can then be used within Ethereum’s vast DeFi ecosystem, including participating in staking protocols on PoS-compatible platforms or lending pools. So, while you’re not staking BTC directly, you are staking a token that represents BTC. This is a key part of understanding what Bitcoin staking is in a DeFi context.
- Advantages: This allows Bitcoin’s value to be utilized in the DeFi space, opening up opportunities for wrapped Bitcoin staking (wBTC) and earning yields that wouldn’t be possible with native BTC. It bridges Bitcoin to other blockchain ecosystems.
- Disadvantages/Risks: This method introduces smart contract risk (vulnerabilities in the code of the DeFi protocol or wBTC contract) and custodian risk (the entity holding the underlying BTC could fail). It also adds a layer of complexity.
4.3. Alternative 3: Centralized exchange “staking” or “savings” programs for Bitcoin
Many centralized cryptocurrency exchanges (CEXs) offer programs labeled as “Bitcoin staking,” “Earn,” or “Savings.” These are often very accessible to users who already have accounts on these Bitcoin staking platforms.

However, it’s important to understand what’s typically happening behind the scenes. In most cases, these are not true staking programs in the PoS sense. Instead, they are often lending programs where the exchange pools users’ deposited Bitcoin and lends it out to other users or institutions, sharing a portion of the interest earned back with the depositors. Sometimes, they might be structured financial products.
- Advantages: These programs are usually user-friendly and easily accessible directly within the exchange interface. They can offer a simple way for beginners to start earning a yield on their Bitcoin.
- Disadvantages/Risks: The term “staking” can be misleading, as it’s often not true staking. You are exposed to the exchange’s counterparty risk (if the exchange goes bankrupt or is hacked). The terms, conditions, and interest rates can also change, and there might be lock-up periods.
4.4. Alternative 4: Yield farming with Bitcoin in DeFi
Yield farming is a more advanced DeFi strategy that can also involve Bitcoin, typically in its wrapped form (like wBTC). It involves providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges (DEXs) or other DeFi protocols.
Users deposit their wBTC (often paired with another cryptocurrency) into a liquidity pool. In return for providing this liquidity, which facilitates trading on the platform, users earn a share of the trading fees generated by that pool and often receive additional reward tokens from the protocol.
- Advantages: Can offer potentially high returns (often referred to as Annual Percentage Yield or APY).
- Disadvantages/Risks: This is one of the more complex and risky methods. It’s susceptible to impermanent loss (where the value of your deposited assets can decrease compared to simply holding them if market prices diverge significantly), smart contract risks, and overall market volatility. It requires a deeper understanding of DeFi mechanics.
Understanding these alternatives to Bitcoin staking is crucial because they represent the practical ways users can currently earn a Bitcoin yield beyond just holding the asset.
5. Potential benefits commonly associated with Bitcoin Staking
While direct Bitcoin staking isn’t feasible, the alternative methods discussed—often collectively (though imprecisely) referred to as Bitcoin staking—can offer several potential benefits for BTC holders. Understanding these advantages can help you evaluate if pursuing such strategies aligns with your financial goals.
- Earning Passive Income: The primary allure is the ability to generate passive income from your existing holdings. Instead of your Bitcoin sitting idle, these methods allow it to potentially earn interest or other rewards over time.
- Potentially Higher Returns than HODLing: For some, these strategies offer the prospect of returns that might exceed simply holding (HODLing) Bitcoin, especially in certain market conditions. However, it’s crucial to remember that higher potential returns almost invariably come with increased risks of Bitcoin staking alternatives.
- Contributing to Other Ecosystems: When engaging in activities like wrapped Bitcoin staking (wBTC) on Proof-of-Stake networks, you are indirectly contributing to the liquidity and security of those other blockchain ecosystems. This can be appealing to users interested in the broader DeFi space.
- Diversifying Crypto Earning Strategies: Utilizing these alternatives can help diversify your cryptocurrency earning strategies beyond just relying on Bitcoin’s price appreciation. It introduces different avenues for potential yield generation.
It’s important to weigh these benefits of Bitcoin staking alternatives against the associated risks, which we will delve into next.
6. Key risks and considerations for Bitcoin Staking alternatives
While the prospect of earning a yield on your Bitcoin through various alternative methods can be attractive, it’s imperative to be acutely aware of the inherent risks of Bitcoin staking alternatives. These are not risk-free endeavors, and thorough due diligence is crucial before committing your assets.
- Counterparty Risk: This is a significant concern when using centralized platforms for Bitcoin lending or “earn” programs. You are entrusting your Bitcoin to a third party (the exchange or lending platform). If that entity becomes insolvent, gets hacked, or engages in mismanagement, your funds could be lost.
- Smart Contract Risk: When interacting with DeFi protocols, especially for wrapped Bitcoin staking (wBTC) or yield farming, you’re exposed to smart contract risk. Bugs or vulnerabilities in the underlying code of these contracts could be exploited, leading to a loss of funds.
- Market Volatility: The cryptocurrency market is notoriously volatile. The value of your deposited Bitcoin, as well as any rewards earned (which might be in BTC or other tokens), can fluctuate dramatically. This can significantly impact the actual returns of your “staking” activities.
- Impermanent Loss: Specifically relevant to yield farming when providing liquidity, impermanent loss occurs when the price of your deposited assets changes compared to when you deposited them. If the price divergence is significant, you might have been better off simply HODLing the assets.
- Lock-up Periods: Some platforms or protocols may require you to lock up your Bitcoin for a specific period to earn yield. During this time, you won’t be able to access or sell your BTC, which can be problematic if you need liquidity or if market conditions change drastically.
- Complexity: Certain methods, particularly in the DeFi space like yield farming or managing wBTC, can be complex and require a good understanding of how these protocols work. Mistakes due to misunderstanding can be costly.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies and related financial services is still evolving globally. Changes in regulations could impact the viability or legality of certain Bitcoin staking alternatives or the platforms offering them.
- It’s Not “True” Bitcoin Staking: Finally, always remember that these methods are not the same as native, on-chain staking found in PoS cryptocurrencies. Understanding this distinction helps manage expectations and correctly assess the mechanisms and risks involved when people discuss what Bitcoin staking is.

Before engaging in any of these strategies, it’s vital to do your own research (DYOR) and never invest more than you can afford to lose.
7. Quick comparison: Bitcoin Staking vs. Bitcoin Mining
To further clarify how earning yield with Bitcoin works, it’s helpful to compare the “Bitcoin staking” alternatives we’ve discussed with the traditional method of acquiring new Bitcoin: Bitcoin mining. While both aim to generate returns, their mechanisms and requirements differ significantly. Understanding the nuances of staking Bitcoin vs mining Bitcoin is key.
Here’s a quick comparison table:
| Feature | Bitcoin Mining | Bitcoin Staking |
| Operating Mechanism | Proof-of-Work (PoW) – solving complex puzzles | Lending, using Wrapped BTC on PoS networks, CEX programs |
| Hardware | Specialized ASICs (expensive, power-hungry) | Minimal (computer/smartphone) |
| Technical Expertise | Very High | Varies (Low for CEX lending, Higher for DeFi) |
| Energy Consumption | Extremely High | Significantly Lower |
| How Rewards Earned | New BTC (block rewards) + transaction fees | Interest, protocol rewards/fees |
| Primary Goal | Secure Bitcoin network, create new BTC | Generate yield on existing BTC |
| Direct Network Role | Core to Bitcoin’s consensus & security | Indirect or on other networks (e.g., wBTC on PoS) |
In detail:
- Operating mechanism:
- Bitcoin Mining: Relies on the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism. Miners use computational power to solve complex puzzles, validate transactions, and secure the Bitcoin network.
- “Bitcoin Staking” Alternatives: Generally involve lending Bitcoin to earn interest, or using wrapped Bitcoin (like wBTC) on Proof-of-Stake (PoS) based platforms or DeFi protocols to earn yield. The underlying mechanism is not Bitcoin’s PoW.
- Hardware requirements:
- Bitcoin Mining: Requires specialized, expensive, and power-hungry hardware known as ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits).
- “Bitcoin Staking” Alternatives: Typically have minimal hardware requirements – often just a computer or smartphone to access platforms.
- Technical expertise:
- Bitcoin Mining: Demands a high level of technical expertise to set up, maintain, and optimize mining operations.
- “Bitcoin Staking” Alternatives: The required expertise varies. Lending on centralized exchanges can be simple, while engaging with DeFi protocols for wBTC staking or yield farming requires a much deeper understanding.
- Energy consumption:
- Bitcoin Mining: Notoriously energy-intensive due to the computational power needed for PoW.
- “Bitcoin Staking” Alternatives: Generally have a significantly lower energy footprint, especially when compared directly to mining, as they often leverage less energy-intensive PoS networks (for wBTC) or are custodial services.
- How rewards are earned:
- Bitcoin Mining: Miners earn newly minted Bitcoin (block rewards) and transaction fees for successfully adding a block to the blockchain.
- “Bitcoin Staking” Alternatives: Rewards are typically earned as interest (from lending) or as protocol rewards/fees (from DeFi activities like staking wBTC or yield farming).
This comparison highlights that while both mining and “staking” alternatives offer ways to accumulate more Bitcoin, they are fundamentally different processes with distinct requirements, risks, and reward structures.
8. Is Bitcoin Staking right for you?
Deciding whether to engage in Bitcoin staking alternatives requires careful consideration of your personal financial situation, risk tolerance, and investment goals. While the allure of earning a Bitcoin yield can be strong, these methods are not suitable for everyone.

Here are some key factors to consider before you proceed:
- Your Risk Tolerance: As detailed earlier, these methods come with various risks, including counterparty risk, smart contract vulnerabilities, and market volatility. Honestly assess how comfortable you are with the potential for loss. If you are highly risk-averse, simply HODLing your Bitcoin might be a more appropriate strategy.
- Your Investment Goals: Are you looking for long-term capital appreciation by holding Bitcoin, or are you seeking to generate active or passive income from Bitcoin from your assets? Your objectives will influence whether the potential rewards from “staking” alternatives outweigh the associated risks and complexities.
- Your Understanding of the Methods: Do not invest in something you don’t understand. Ensure you have a solid grasp of how a specific lending platform, DeFi protocol, or wBTC mechanism works, including all associated risks of Bitcoin staking alternatives, before committing any funds.
- The Importance of DYOR (Do Your Own Research): This cannot be stressed enough. Thoroughly research any platform or protocol you are considering. Read reviews, understand their security measures, check their terms and conditions, and be wary of promises of unusually high returns, as these often correlate with higher risk.
Ultimately, the decision is yours. H2T Finance aims to provide comprehensive, neutral information to help you understand concepts like what Bitcoin staking is, but we do not offer financial advice. Always make informed decisions based on your own research and circumstances.
8. FAQ about Bitcoin Staking
To help further clarify common queries surrounding what Bitcoin staking is, here are answers to some frequently asked questions:
To be clear, can I stake my Bitcoin directly on the Bitcoin blockchain?
No, you cannot. The Bitcoin network operates using the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which does not support staking in the way Proof-of-Stake (PoS) networks do. When people refer to “Bitcoin staking,” they are usually talking about alternative methods to earn a yield on their Bitcoin, not direct on-chain staking.
Is Bitcoin staking (through alternatives) safe?
The safety level varies significantly depending on the method chosen and the platform used. Lending Bitcoin or engaging with DeFi protocols for wrapped Bitcoin staking (wBTC) involves inherent risks. These include counterparty risk (the platform failing), smart contract vulnerabilities (exploitable flaws in code), and market volatility. No method of earning yield on crypto is entirely risk-free.
How much can I earn from Bitcoin staking alternatives?
Potential earnings, often expressed as an Annual Percentage Yield (APY), differ widely. Factors influencing returns include the specific platform or protocol, the chosen method (e.g., lending vs. yield farming), current market conditions, and the level of risk you are willing to undertake. Generally, higher potential Bitcoin staking rewards come with higher risks.
What’s the difference between just holding Bitcoin (HODLing) and Bitcoin staking alternatives?
HODLing means simply keeping your Bitcoin in a secure wallet, primarily anticipating price appreciation over the long term. Bitcoin staking alternatives, on the other hand, are active strategies aimed at generating additional Bitcoin or other crypto assets from your existing holdings. While potentially increasing your holdings, these alternatives also introduce new layers of risk and complexity compared to just HODLing.
Where can I “stake” Bitcoin?
Since native Bitcoin cannot be staked, you would explore platforms that offer the alternatives discussed. This could include centralized exchanges for Bitcoin lending or “savings” programs, DeFi lending protocols, or platforms facilitating the use and staking of wrapped Bitcoin (wBTC) on PoS-compatible networks. It is crucial to thoroughly research any platform before depositing funds. H2T Finance does not endorse or recommend any specific Bitcoin staking platforms.
Conclusion
In essence, while Bitcoin staking is a commonly mentioned term, it’s important to note that native Bitcoin (BTC) cannot be staked directly on its Proof-of-Work blockchain like Proof-of-Stake (PoS) coins. Instead, it refers to various alternative strategies such as Bitcoin lending, using wrapped Bitcoin (wBTC) on PoS networks, or participating in centralized exchange savings programs.
Each of these methods has its own mechanisms and risks, making it crucial to understand them before committing your assets. In the cryptocurrency landscape, informed decision-making is vital, so continue your research and prioritize investment security.
Ready to expand your crypto knowledge further? Explore more foundational crypto concepts in our Bitcoin section. Stay updated with the latest insights from Viet Nam – US Trade by subscribing to our newest blog!





